It looks like you're using an Ad Blocker.
Please white-list or disable AboveTopSecret.com in your ad-blocking tool.
Thank you.
Some features of ATS will be disabled while you continue to use an ad-blocker.
4
share:
web.mit.edu...
An international team, led by researchers at MIT's Haystack Observatory, has for the first time measured the radius of a black hole at the center of a distant galaxy—the closest distance at which matter can approach before being irretrievably pulled into the black hole. The scientists linked together radio dishes in Hawaii, Arizona and California to create a telescope array called the "Event Horizon Telescope" (EHT) that can see details 2,000 times finer than what's visible to the Hubble Space Telescope. These radio dishes were trained on M87, a galaxy some 50 million light years from the Milky Way. M87 harbors a black hole 6 billion times more massive than our sun; using this array, the team observed the glow of matter near the edge of this black hole—a region known as the "event horizon."
The team used a technique called Very Long Baseline Interferometry, or VLBI, which links data from radio dishes located thousands of miles apart. Signals from the various dishes, taken together, create a "virtual telescope" with the resolving power of a single telescope as big as the space between the disparate dishes. The technique enables scientists to view extremely precise details in faraway galaxies.
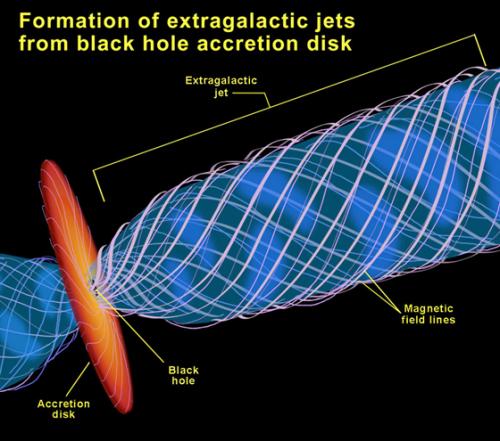
Jets at the edge of a black hole.
Supermassive black holes are the most extreme objects predicted by Albert Einstein's theory of gravity—where, according to Doeleman, "gravity completely goes haywire and crushes an enormous mass into an incredibly close space." At the edge of a black hole, the gravitational force is so strong that it pulls in everything from its surroundings. However, not everything can cross the event horizon to squeeze into a black hole. The result is a "cosmic traffic jam" in which gas and dust build up, creating a flat pancake of matter known as an accretion disk. This disk of matter orbits the black hole at nearly the speed of light, feeding the black hole a steady diet of superheated material. Over time, this disk can cause the black hole to spin in the same direction as the orbiting material.
What can this information and technique be used for?
www.dailygalaxy.com...
Testing General Relativity.
A jet's trajectory may help scientists understand the dynamics of black holes in the region where their gravity is the dominant force. Doeleman says such an extreme environment is perfect for confirming Einstein's theory of general relativity—today's definitive description of gravitation. "Einstein's theories have been verified in low-gravitational field cases, like on Earth or in the solar system," Doeleman says. "But they have not been verified precisely in the only place in the universe where Einstein's theories might break down—which is right at the edge of a black hole."
Edit: Discuss theories of gravity, and/or black holes. For my own personal take on black hole creation scroll down 2 posts and you will find it.
edit on 29-9-2012 by ubeenhad because: (no reason given)
edit on Sat Sep 29 2012 by DontTreadOnMe because:
IMPORTANT: Using Content From Other Websites on ATS
edit on Sat Sep 29
2012 by DontTreadOnMe because: (no reason given)
Starting a New Thread?...Look Here
First AboveTopSecret.com takes pride in making every post count.
Please do not create minimal posts to start your new thread.
If you feel inclined to make the board aware of news, current events,
or important information from other sites
please post one or two paragraphs,
a link to the entire story,
AND your opinion, twist or take on the news item,
as a means to inspire discussion or collaborative research on your subject.
edit on Sat Sep 29 2012 by DontTreadOnMe because: (no reason given)
I'd say we need to focus much more on our own Solar System and getting Boots on the Soil to the planets around us....then when we have learned to
walk, we need to run out there to the great expanse and explore things like Black Holes. So fascinating and I can't wait for the future generations
which will know a world with the material science and technology for propulsion to get to these things and debate how to send probes near or into for
more information.
Someday...and isn't it a day to dream for.
Someday...and isn't it a day to dream for.
reply to post by ubeenhad
star and flag op,
it is customary to give a few lines describing the implications of the paper or findings,
and maybe some things in the science field, that these findings would/could effect ect.
please feel free to add a conspiratorial angle, if you like
it helps breed discussion
i can finally accept black holes are real and not just speculations
thank you
xploder
star and flag op,
it is customary to give a few lines describing the implications of the paper or findings,
and maybe some things in the science field, that these findings would/could effect ect.
please feel free to add a conspiratorial angle, if you like
it helps breed discussion
i can finally accept black holes are real and not just speculations
thank you
xploder
reply to post by XPLodER
I mentioned in another thread that with the limits of experimental particle physics approaching, extreme-gravity astrophysical observations are going to be the future of fundamental physics.
I would like to add my own bit of scientific speculation. Normally ideas like this don't have a venue to be told until you got some observations or some handy math. So ill take advantage of the situation.
This is my original facebook message to a friend I sent it on 1/17/2008. Should give the details..
"think about a second big bang as the creation of a black hole from the interior. On the outside of the horizon there is our universe, full of matter and energy. In our universe stuff slowly goes into the black hole seemingly not moving at all but to the inflow material time is running normal, so it seems like stuff is falling in before and after you but from the outside the flow looks frozen. Well if we fast forward in the inflows reference frame, and our point of reference is around some of the first material to fall in, we could imagine seeing a new portion of space time being created. this first "bubble" would be the quark-gluon plasma, So were does the inflation come from? Some critical density reached when enough material as fallen through causes the explosion of inflation at a couple miliseconds into the life of the universe, or in this case, a new region of space time, that will continue to grow and make black holes were energy and matter fall into creating new regions of space time. Because of the difference in time, conservation of energy is still maintained over the entire system because its all from the same "bank", just spread out over "time zones"
The difference in time dialation between outside material and inflow material compared to the rate of expansion of the early quark gluon universe before the secondary inflation it could be used to find the "critical density" that would be needed to cause inflation and that could give us testable predictions.
I dont know why similar thought isnt taken more seriously. maybe because the recent developments in particle physics has made people shy away from gravity, un quantized, and theories like these have no experimental basis. which is fine for most quantum theories of gravity cause there is enough math that goes together to make you suspicious. But things like this have less to explain by and are more intuitive conceptual stuff. I think this is why string theory and loop quantum gravity have support, cause they found little mathmatical curiosities. Well what about the conceptual curiosities. I cant get over the correlation with creating new regions of space/time. Thats one thing every big bang supporter must agree on, that it created new regions of space. Well what is the only other known object in the universe shares the same traits. BLACK HOLES. So as a black hole eats, the unstoppable force of gravity keeps pulling more and more energy into the black hole. Some property of space under these conditions only allow for certain "critical density". Once that is reached, BANG, space expands and the black hole is cut off. Now back in the original universe time is going by as normal and matter slowly goes into the black hole. Because of such a drastic difference in time frames it seems mathmatically possible to never loose the conservation of energy over the entire system, even with an infinite amount of "total time"."
Very rough, and raw. Havent had the time to pursue but still to this day, some of the points I made I still cant shake. It was to a laymen, so excuse some of the terminology and over simplification.
I mentioned in another thread that with the limits of experimental particle physics approaching, extreme-gravity astrophysical observations are going to be the future of fundamental physics.
I would like to add my own bit of scientific speculation. Normally ideas like this don't have a venue to be told until you got some observations or some handy math. So ill take advantage of the situation.
This is my original facebook message to a friend I sent it on 1/17/2008. Should give the details..
"think about a second big bang as the creation of a black hole from the interior. On the outside of the horizon there is our universe, full of matter and energy. In our universe stuff slowly goes into the black hole seemingly not moving at all but to the inflow material time is running normal, so it seems like stuff is falling in before and after you but from the outside the flow looks frozen. Well if we fast forward in the inflows reference frame, and our point of reference is around some of the first material to fall in, we could imagine seeing a new portion of space time being created. this first "bubble" would be the quark-gluon plasma, So were does the inflation come from? Some critical density reached when enough material as fallen through causes the explosion of inflation at a couple miliseconds into the life of the universe, or in this case, a new region of space time, that will continue to grow and make black holes were energy and matter fall into creating new regions of space time. Because of the difference in time, conservation of energy is still maintained over the entire system because its all from the same "bank", just spread out over "time zones"
The difference in time dialation between outside material and inflow material compared to the rate of expansion of the early quark gluon universe before the secondary inflation it could be used to find the "critical density" that would be needed to cause inflation and that could give us testable predictions.
I dont know why similar thought isnt taken more seriously. maybe because the recent developments in particle physics has made people shy away from gravity, un quantized, and theories like these have no experimental basis. which is fine for most quantum theories of gravity cause there is enough math that goes together to make you suspicious. But things like this have less to explain by and are more intuitive conceptual stuff. I think this is why string theory and loop quantum gravity have support, cause they found little mathmatical curiosities. Well what about the conceptual curiosities. I cant get over the correlation with creating new regions of space/time. Thats one thing every big bang supporter must agree on, that it created new regions of space. Well what is the only other known object in the universe shares the same traits. BLACK HOLES. So as a black hole eats, the unstoppable force of gravity keeps pulling more and more energy into the black hole. Some property of space under these conditions only allow for certain "critical density". Once that is reached, BANG, space expands and the black hole is cut off. Now back in the original universe time is going by as normal and matter slowly goes into the black hole. Because of such a drastic difference in time frames it seems mathmatically possible to never loose the conservation of energy over the entire system, even with an infinite amount of "total time"."
Very rough, and raw. Havent had the time to pursue but still to this day, some of the points I made I still cant shake. It was to a laymen, so excuse some of the terminology and over simplification.
edit on 29-9-2012 by ubeenhad because: (no reason given)
Originally posted by ubeenhad
reply to post by XPLodER
I mentioned in another thread that with the limits of experimental particle physics approaching, extreme-gravity astrophysical observations are going to be the future of fundamental physics.
something to take into account is the density of the region of space that these observations occur,
and the optical implications of densely packed refractive elements within this reigion of space


"think about a second big bang as the creation of a black hole from the interior. On the outside of the horizon there is our universe, full of matter and energy. In our universe stuff slowly goes into the black hole seemingly not moving at all but to the inflow material time is running normal, so it seems like stuff is falling in before and after you but from the outside the flow looks frozen. Well if we fast forward in the inflows reference frame, and our point of reference is around some of the first material to fall in, we could imagine seeing a new portion of space time being created. this first "bubble" would be the quark-gluon plasma, So were does the inflation come from? Some critical density reached when enough material as fallen through causes the explosion of inflation at a couple miliseconds into the life of the universe, or in this case, a new region of space time, that will continue to grow and make black holes were energy and matter fall into creating new regions of space time. Because of the difference in time, conservation of energy is still maintained over the entire system because its all from the same "bank", just spread out over "time zones"
IMHO it is the vibrations of the components within the quark/gluon plasma, and the induced energy from this vibration in the density that allows the interactions between these parts,
motion, vibration
field, space inhabited
conductor, quark gluon integration of spin/motion with energy equalisation
time being relative to the scale of the observed and the observer
The difference in time dialation between outside material and inflow material compared to the rate of expansion of the early quark gluon universe before the secondary inflation it could be used to find the "critical density" that would be needed to cause inflation and that could give us testable predictions.
cern has been producing quark gluon plasma for a while now and the data sets are increasing in size,
at the speeds being approached i suspect a critical density will be just out of reach at the speeds close to the speed of light. this comes about because of time dialation.
I dont know why similar thought isnt taken more seriously. maybe because the recent developments in particle physics has made people shy away from gravity, un quantized, and theories like these have no experimental basis. which is fine for most quantum theories of gravity cause there is enough math that goes together to make you suspicious. But things like this have less to explain by and are more intuitive conceptual stuff. I think this is why string theory and loop quantum gravity have support, cause they found little mathmatical curiosities. Well what about the conceptual curiosities. I cant get over the correlation with creating new regions of space/time. Thats one thing every big bang supporter must agree on, that it created new regions of space. Well what is the only other known object in the universe shares the same traits. BLACK HOLES. So as a black hole eats, the unstoppable force of gravity keeps pulling more and more energy into the black hole. Some property of space under these conditions only allow for certain "critical density". Once that is reached, BANG, space expands and the black hole is cut off. Now back in the original universe time is going by as normal and matter slowly goes into the black hole. Because of such a drastic difference in time frames it seems mathmatically possible to never loose the conservation of energy over the entire system, even with an infinite amount of "total time"."
gravity has for a long time been a fix all catch all for how the universe interacts with mass in terms of rest mass/inertial mass, for an observer using gravity to quantify "visual" observations, that by there very nature are skewed because light (allowing our observations) is also effected by the very mass we are trying to study.
without acknowledging that optical density can effect these light based observations, we wrongly conclude extra inertial or rest mass as the suspect for the skewed observations.
suns give of energy in sigmoid curve,
black holes consume energy in a equatorial toroid shape and is sporadic depending on a number of factors,
i believe the difference in consumption of energy and the creation of energy leads to the shape of our galaxy
and galaxy clusters shape our universe
xploder
edit on 29-9-2012 by XPLodER because: (no reason given)
edit on 29-9-2012 by XPLodER because: (no reason
given)
Originally posted by XPLodER
IMHO it is the vibrations of the components within the quark/gluon plasma, and the induced energy from this vibration in the density that allows the interactions between these parts,
motion, vibration
field, space inhabited
conductor, quark gluon integration of spin/motion with energy equalisation
time being relative to the scale of the observed and the observer
Im confused. Are you just giving your view on the characteristics of a QGP or are you disagreeing with something?
cern has been producing quark gluon plasma for a while now and the data sets are increasing in size, at the speeds being approached i suspect a critical density will be just out of reach at the speeds close to the speed of light. this comes about because of time dialation.
To experimentally test, obviously. Im talking about using the different inflation models to find a correlation between the inflation rate of a black hole from the interior of the horizon, and the universe.
Some property of space allows inflation, correct me if im wrong we can describe it but not give a mechanism to it.
black holes consume energy in a equatorial toroid shape and is sporadic depending on a number of factors,
i believe the difference in consumption of energy and the creation of energy leads to the shape of our galaxy
Irrelevant. Not every new area of spacetime would have to reach inflation. Not every new area of spacetime has to have the same amount of "stuff"
Active galactiv nucluei fueling the expansion of the universe, doing other things stuff. Is that what you mean by shaping and what not.
Are you talking about the ideas put forth by the guy who claimed quasars were much closer and their redshift was due to something else, I cant remember the details. It was falsified by other types of measurments I believe.
edit on 29-9-2012 by ubeenhad because: (no reason given)
edit on 29-9-2012 by ubeenhad because: (no reason
given)
edit on 29-9-2012 by ubeenhad because: (no reason given)
Im confused. Are you just giving your view on the characteristics of a QGP or are you disagreeing with something?
i have some problems with the definitions used in QGP but that is for another thread altogether
To experimentally test, obviously. Im talking about using the different inflation models to find a correlation between the inflation rate of a black hole from the interior of the horizon, and the universe.
you mean using a model that conforms to whos version of "what happens at an event horizon"? hawkings?
Some property of space allows inflation, correct me if im wrong we can describe it but not give a mechanism to it.
pre subscribing to "the thought inflation exists beyond an optical/gravitational lensing effect" ,
you can see its presence in the way galaxies move away from each other so fast it cant be accounted for with all known mass and or energy sources, in effect breaking the conservation of energy principals held so dear to physics and thermodynamic community. note< i have not said "redshift doesn't equal distance"
Irrelevant. Not every new area of spacetime would have to reach inflation. Not every new area of spacetime has to have the same amount of "stuff"
in current models in large scales the universe is predicted to be homogeneous, but space at the same time would have to be expanding to account for the speed at which objects would have to move away from each other in the manner they "look" too considering their "redshift"
Active galactiv nucluei fueling the expansion of the universe, doing other things stuff. Is that what you mean by shaping and what not.
yes, if there are bubbles around galaxies and we can measure the interface between "inside and outside"
the interactions at interface may provide mechanical energy, attraction repulsion, rotation or orbit, sling shot ect
Are you talking about the ideas put forth by the guy who claimed quasars were much closer and their redshift was due to something else, I cant remember the details. It was falsified by other types of measurements I believe.
halton arp is the guy and no.
i just suggest optics plays a much larger part in our observations, than it is currently being given at astrophysical scales.
xploder
edit on 29-9-2012 by XPLodER because: (no reason given)
edit on 29-9-2012 by XPLodER because: (no reason
given)
new topics
-
A Warning to America: 25 Ways the US is Being Destroyed
New World Order: 13 minutes ago -
America's Greatest Ally
General Chit Chat: 58 minutes ago -
President BIDEN's FBI Raided Donald Trump's Florida Home for OBAMA-NORTH KOREA Documents.
Political Conspiracies: 5 hours ago -
Maestro Benedetto
Literature: 7 hours ago -
Is AI Better Than the Hollywood Elite?
Movies: 7 hours ago -
Las Vegas UFO Spotting Teen Traumatized by Demon Creature in Backyard
Aliens and UFOs: 11 hours ago -
2024 Pigeon Forge Rod Run - On the Strip (Video made for you)
Automotive Discussion: 11 hours ago
top topics
-
President BIDEN's FBI Raided Donald Trump's Florida Home for OBAMA-NORTH KOREA Documents.
Political Conspiracies: 5 hours ago, 26 flags -
Krystalnacht on today's most elite Universities?
Social Issues and Civil Unrest: 17 hours ago, 9 flags -
Gaza Terrorists Attack US Humanitarian Pier During Construction
Middle East Issues: 12 hours ago, 8 flags -
Supreme Court Oral Arguments 4.25.2024 - Are PRESIDENTS IMMUNE From Later Being Prosecuted.
Above Politics: 17 hours ago, 8 flags -
Weinstein's conviction overturned
Mainstream News: 15 hours ago, 8 flags -
Massachusetts Drag Queen Leads Young Kids in Free Palestine Chant
Social Issues and Civil Unrest: 14 hours ago, 7 flags -
Las Vegas UFO Spotting Teen Traumatized by Demon Creature in Backyard
Aliens and UFOs: 11 hours ago, 6 flags -
Meadows, Giuliani Among 11 Indicted in Arizona in Latest 2020 Election Subversion Case
Mainstream News: 14 hours ago, 5 flags -
2024 Pigeon Forge Rod Run - On the Strip (Video made for you)
Automotive Discussion: 11 hours ago, 4 flags -
Is AI Better Than the Hollywood Elite?
Movies: 7 hours ago, 3 flags
active topics
-
Massachusetts Drag Queen Leads Young Kids in Free Palestine Chant
Social Issues and Civil Unrest • 15 • : tarantulabite1 -
A Warning to America: 25 Ways the US is Being Destroyed
New World Order • 0 • : charlest2 -
America's Greatest Ally
General Chit Chat • 1 • : BingoMcGoof -
How ageing is" immune deficiency"
Medical Issues & Conspiracies • 35 • : annonentity -
HORRIBLE !! Russian Soldier Drinking Own Urine To Survive In Battle
World War Three • 49 • : Freeborn -
Gaza Terrorists Attack US Humanitarian Pier During Construction
Middle East Issues • 30 • : Asher47 -
Electrical tricks for saving money
Education and Media • 8 • : anned1 -
Is AI Better Than the Hollywood Elite?
Movies • 16 • : 5thHead -
Hate makes for strange bedfellows
US Political Madness • 48 • : Terpene -
President BIDEN's FBI Raided Donald Trump's Florida Home for OBAMA-NORTH KOREA Documents.
Political Conspiracies • 17 • : BingoMcGoof
4