It looks like you're using an Ad Blocker.
Please white-list or disable AboveTopSecret.com in your ad-blocking tool.
Thank you.
Some features of ATS will be disabled while you continue to use an ad-blocker.
25
share:
Second Solar System Like Ours Discovered
by Shannon Hall on November 27, 2013
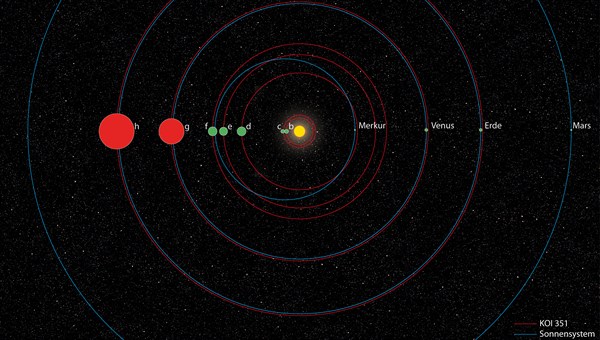
A team of European astronomers has discovered a second solar system, the closest parallel to our own solar system yet found. It includes seven exoplanets orbiting a star with the small rocky planets close to their host star and the gas giant planets further away. The system was hidden within the wealth of data from the Kepler Space Telescope.
KOI-351 is “the first system with a significant number of planets (not just two or three, where random fluctuations can play a role) that shows a clear hierarchy like the solar system — with small, probably rocky, planets in the interior and gas giants in the (exterior),” Dr. Juan Cabrera, of the Institute of Planetary Research at the German Aerospace Center, told Universe Today.
Three of the seven planets orbiting KOI-351 were detected earlier this year, and have periods of 59, 210 and 331 days — similar to the periods of Mercury, Venus and Earth.
But the orbital periods of these planets vary by as much as 25.7 hours. This is the highest variation detected in an exoplanet’s orbital period so far, hinting that there are more planets than meets the eye.
While astronomers have discovered over 1000 exoplanets, this is the first solar system analogue detected to date. Not only are there seven planets, but they display the same architecture — rocky small planets orbiting close to the sun and gas giants orbiting further away — as our own solar system.
Read more: www.universetoday.com...
www.universetoday.com...
The Planetary System to KIC 11442793: A Compact Analogue to the Solar System
J. Cabrera, Sz. Csizmadia, H. Lehmann, R. Dvorak, D. Gandolfi, H. Rauer, A. Erikson, C. Dreyer, Ph. Eigmueller, A. Hatzes
(Submitted on 23 Oct 2013 (v1), last revised 11 Nov 2013 (this version, v2))
arxiv.org...
Full PDF ..
arxiv.org...
J. Cabrera, Sz. Csizmadia, H. Lehmann, R. Dvorak, D. Gandolfi, H. Rauer, A. Erikson, C. Dreyer, Ph. Eigmueller, A. Hatzes
(Submitted on 23 Oct 2013 (v1), last revised 11 Nov 2013 (this version, v2))
arxiv.org...
Full PDF ..
arxiv.org...
We announce the discovery of a planetary system with 7 transiting planets around a Kepler target, a current record for transiting systems. Planets b, c, e and f are reported for the first time in this work. Planets d, g and h were previously reported in the literature (Batalha et al. 2013), although here we revise their orbital parameters and validate their planetary nature. Planets h and g are gas giants and show strong dynamical interactions. The orbit of planet g is perturbed in such way that its orbital period changes by 25.7h between two consecutive transits during the length of the observations, which is the largest such perturbation found so far. The rest of the planets also show mutual interactions: planets d, e and f are super-Earths close to a mean motion resonance chain (2:3:4), and planets b and c, with sizes below 2 Earth radii, are within 0.5% of the 4:5 mean motion resonance. This complex system presents some similarities to our Solar System, with small planets in inner orbits and gas giants in outer orbits. It is, however, more compact. The outer planet has an orbital distance around 1 AU, and the relative position of the gas giants is opposite to that of Jupiter and Saturn, which is closer to the expected result of planet formation theories. The dynamical interactions between planets are also much richer.
reply to post by MariaLida
That's a really neat find, by them & you!
I've read the source article but can't seem to find where this system is located. I must have missed it.
Do you know where it's located?
That's a really neat find, by them & you!
I've read the source article but can't seem to find where this system is located. I must have missed it.
Do you know where it's located?
Riffrafter
reply to post by MariaLida
That's a really neat find, by them & you!
I've read the source article but can't seem to find where this system is located. I must have missed it.
Do you know where it's located?
Dwarf star, known as KIC 11442793 ..
2,500 light-years from the Earth ..
Wow
I wanna go I wanna go
Where do I sign up!
All jokes aside this is an awesome find
S+F
I wanna go I wanna go
Where do I sign up!
All jokes aside this is an awesome find
S+F
Cobaltic1978
Great, let's get there!
Nuuuuuuuuu...
Why. If they said "An island in the pacific ocean like a smaller version of Australia!" would yuo want to go get eaten by the bugs and animals and humans?
That's basically all this is.. except the bugs and animals and humans.
Outer space is chock full of solar systems. This one so far seems pretty comfortable. I rekon we stay here.
reply to post by theantediluvian
Maybe one day ..
We find some way )
Maybe not there, but somewhere closer yes way not ..
I truly believe in that, but only if we in first place don't destroy the "basics" here for the next generations ..
Maybe one day ..
We find some way )
Maybe not there, but somewhere closer yes way not ..
I truly believe in that, but only if we in first place don't destroy the "basics" here for the next generations ..
Riffrafter
reply to post by MariaLida
I've read the source article but can't seem to find where this system is located. I must have missed it.
Do you know where it's located?
According to the below source, KOI-351 is 2721 ly away from our solar sytem
www.openexoplanetcatalogue.com...
It's very annoying, the number of lazily-written articles about objects in space, which don't provide this basic piece of information. Craptastic journalism abounds in all fields these days.
edit on 27-11-2013 by MrInquisitive because: (no reason given)
So how far away is the system in question?
Any chance we will be able to send a probe in its direction if we ever get this Alcubierre drive concept off the paper and into production?
Any chance we will be able to send a probe in its direction if we ever get this Alcubierre drive concept off the paper and into production?
edit on 28-11-2013 by andy06shake because: (no reason given)
reply to post by MariaLida
Interesting piece of info.
I wonder if this is where we have our "other Earth" teaming with Life just like our own but hopefully not ruled by an Elite select!
A long way off though, can't visit unless we invent some type of System which can propel a ship to great distances!
I wonder if its possible to ride on Asteroids/Comets through Space... take a ride on one and then when we reach a point where we can transfer over to another one (to take us further), light up the boosters and latch onto it... ride that one until we see another one and repeat.
Interesting piece of info.
I wonder if this is where we have our "other Earth" teaming with Life just like our own but hopefully not ruled by an Elite select!
A long way off though, can't visit unless we invent some type of System which can propel a ship to great distances!
I wonder if its possible to ride on Asteroids/Comets through Space... take a ride on one and then when we reach a point where we can transfer over to another one (to take us further), light up the boosters and latch onto it... ride that one until we see another one and repeat.
new topics
-
Only two Navy destroyers currently operational as fleet size hits record low
Military Projects: 2 hours ago -
George Stephanopoulos and ABC agree to pay $15 million to settle Trump defamation suit
Mainstream News: 7 hours ago
top topics
-
George Stephanopoulos and ABC agree to pay $15 million to settle Trump defamation suit
Mainstream News: 7 hours ago, 16 flags -
Light from Space Might Be Travelling Instantaneously
Space Exploration: 15 hours ago, 9 flags -
The MSM has the United Healthcare assassin all wrong.
General Conspiracies: 16 hours ago, 8 flags -
More Bad News for Labour and Rachel Reeves Stole Christmas from Working Families
Regional Politics: 14 hours ago, 8 flags -
2025 Bingo Card
The Gray Area: 16 hours ago, 7 flags -
Only two Navy destroyers currently operational as fleet size hits record low
Military Projects: 2 hours ago, 6 flags
active topics
-
Former DNI-Congressman John Ratcliffe says the U.S. Government is Intimidated by UFOs.
Aliens and UFOs • 40 • : Astrocometus -
The Mystery Drones and Government Lies
Political Conspiracies • 71 • : cherokeetroy -
-@TH3WH17ERABB17- -Q- ---TIME TO SHOW THE WORLD--- -Part- --44--
Dissecting Disinformation • 3683 • : duncanagain -
One out of every 20 Canadians Dies by Euthanasia
Medical Issues & Conspiracies • 23 • : Daughter2v2 -
Drones everywhere in New Jersey
Aliens and UFOs • 165 • : Zaphod58 -
Mass UAP events. DC. Machester Airport, UFOs over sub base in CT, Nuke bases.
Aliens and UFOs • 57 • : WeMustCare -
FBI Director CHRISTOPHER WRAY Will Resign Before President Trump Takes Office on 1.20.2025.
US Political Madness • 26 • : WeMustCare -
George Stephanopoulos and ABC agree to pay $15 million to settle Trump defamation suit
Mainstream News • 10 • : WeMustCare -
President-Elect DONALD TRUMP's 2nd-Term Administration Takes Shape.
Political Ideology • 330 • : WeMustCare -
Light from Space Might Be Travelling Instantaneously
Space Exploration • 24 • : norhoc4
25
