It looks like you're using an Ad Blocker.
Please white-list or disable AboveTopSecret.com in your ad-blocking tool.
Thank you.
Some features of ATS will be disabled while you continue to use an ad-blocker.
11
share:

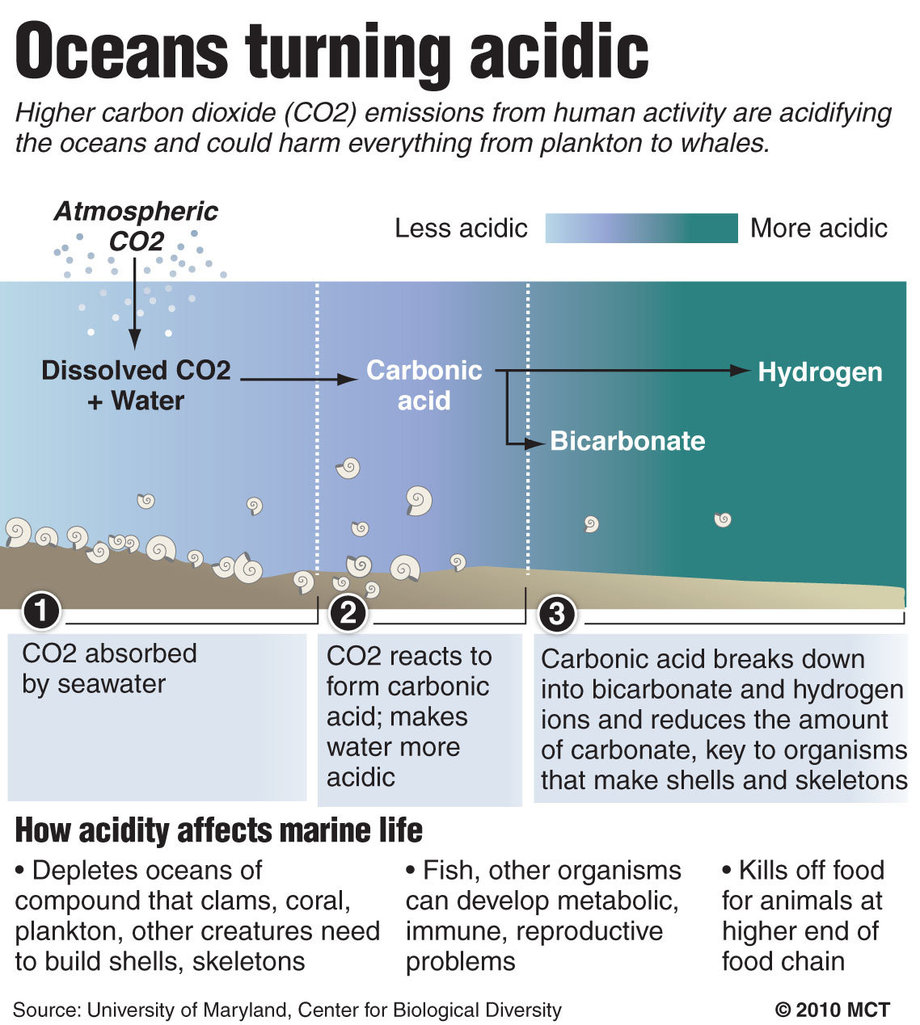
Earth’s greatest extinction event happened in a one-two punch 252 million years ago. Research now suggests that the second pulse of extinction, during which nearly all marine species vanished from the planet, happened in the wake of huge volcanic eruptions that spewed out carbon dioxide and made the oceans more acidic.
Source
The article articles states that a mass extinction that occurred around 252 million years ago, wiped out more than 90% of marine life and more than two-thirds of the animals living on land.
After a period of extreme volcanic activity the ocean began to absorb large amounts of carbon dioxide. Over time the chemical composition of the oceans had changed, becoming more acidic with led to the death of almost all marine life.
The Permian-Triassic Boundary extinction took place over a 60,000 year period, researchers say. Acidification of the oceans lasted for around 10,000 years.
Scientists are using this new study to understand how ocean acidification is occurring today. The amazing thing is they say the carbon was released at a similar rate to today's emissions.
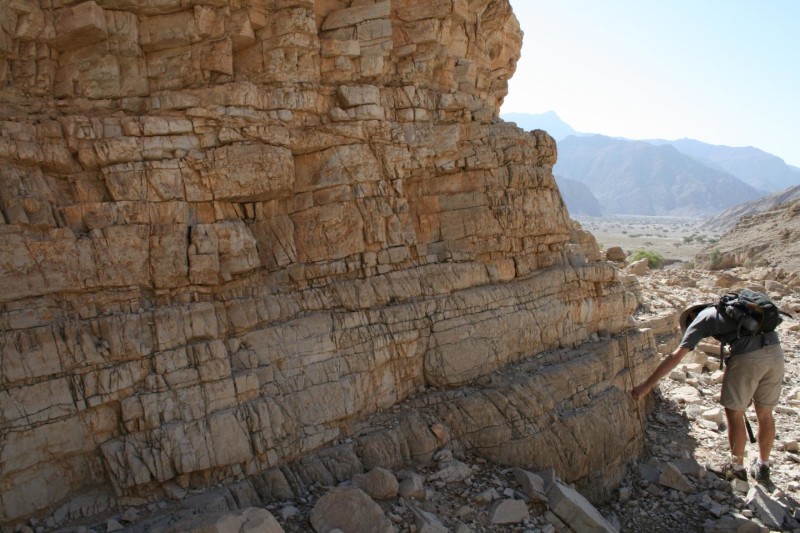

The team analyzed rocks unearthed in the United Arab Emirates - which were on the ocean floor at the time - to develop a climate model to work out what drove the extinction. The rocks preserve a detailed record of changing oceanic conditions at the time.
For anyone interested, the study was published in the journal Science and was a collaboration between the University of Bremen, Germany, Exeter as well as the Universities of Graz, Leeds, and Cambridge.
Funding was provided by the International Centre for Carbonate Resovoirs, Natural Environment Research Council, The Leverhulme Trust, German Research Foundation and the Marsden Fund. Those names might come in handy because here comes the fork in the road...
Dr Matthew Clarkson, of the University of Edinburgh's School of GeoSciences, who coordinated the study, said: "Scientists have long suspected that an ocean acidification event occurred during the greatest mass extinction of all time, but direct evidence has been lacking until now. This is a worrying finding, considering that we can already see an increase in ocean acidity today that is the result of human carbon emissions."
Looks like no matter how hard we try to cut back our emissions, we are at the mercy of Earth and her geological temper tantrums. Could our actions inadvertently cause a volcano to erupt? What if we accidentally set off a chain of events during an attempt at fracking or testing a nuclear warhead underground?
Ironically, there is a whole other side to this mass extinction event. Just like performing a controlled burn to make way for new growth, where their is death, new life will arise from it's ashes.
New evidence shows carbon's importance to ocean life's survival 252 million years ago
A new study led by scientists with The University of Texas at Arlington demonstrates for the first time how elemental carbon became an important construction material of some forms of ocean life after one of the greatest mass extinctions in the history of Earth more than 252 million years ago.
Humans, whether they were put here, from dust or evolved from single celled organisms, really don't have much control over anything. The more we learn and experiment with Earth's natural processes, the more harm than good I think we do. We are selfish to think we hold dominion over such a more biologically complex life form.
"Much of the volcanic activity was connected with the extensive Siberian flood basalt known as the Siberian Traps that emerged through Permian aged coal deposits and, of course, the burning of coal created CO2," Nestell said.
I don't have the answer to the worlds energy troubles, but I do think there is technology being suppressed that could save us from ourselves in the immediate. Its all used to control the planet and the evolution of our species. Only a few select groups are allowed to grow beyond what you currently see and use their new attributes to maintain a choke hold on the rest of us.

After most animals died from lack of oxygen, the remaining microorganisms thrived from the increase in carbon dioxide left in the atmosphere and oceans. I game of tug of war took place between the these cycles and eventually enough carbon dioxide was absorbed, giving birth to an oxygen rich environment for new complex life to form.

You will hear of the sea turning black, and many living things dying because of it. - Hopi Prophesy
Welcome to the beginning of the end. We are slowly killing our planet, but will not die by our own hand. If we continue to poke the bear long enough we are going to get what we deserve. A total reset of the human race. Be kind to others and enjoy every day like it was your last.
Please enjoy this great video about our "Mother" and share you thoughts. I do not support or deny this claim, but found it intriguing enough to share. Thanks for reading.
"The underlying principle of Balance in Nature’s One Law is equality of interchange between the pairs of opposites in any transaction in Nature." - Walter Russell
edit on 11-4-2015 by eisegesis because: (no reason given)
a reply to: eisegesis
So what set off all these volcanoes?
My guess is big impactor.
In Lucifers Hammer the scientists they consulted recognized that any really large impact by an asteroid would generate shock waves sufficient to trigger massive earthquakes and volcanoes. Not only but on its own generate enough sulfides in the atmosphere to poison all the oceans on the planet, depending on how big it was and where it hit. Since the earths surface is mostly ocean…
in the wake of huge volcanic eruptions that spewed out carbon dioxide and made the oceans more acidic.
So what set off all these volcanoes?
My guess is big impactor.
In Lucifers Hammer the scientists they consulted recognized that any really large impact by an asteroid would generate shock waves sufficient to trigger massive earthquakes and volcanoes. Not only but on its own generate enough sulfides in the atmosphere to poison all the oceans on the planet, depending on how big it was and where it hit. Since the earths surface is mostly ocean…
edit on 11-4-2015 by intrptr
because: spelling
So this mass extinction event 250 million years ago (a time as far as I'm told where no cars and factories existed) was caused by volcanoes
acidifying the oceans. Surely you see where I'm going with this?
a reply to: intrptr
Lucifer's hammer, that sounds fitting. It could also be gases building from below the surface. This cycle was likely to repeat many times. Death from above/below...
Dark Matter May Have Caused Earth’s Cataclysms, Mass Extinctions
Which hurts less?
Lucifer's hammer, that sounds fitting. It could also be gases building from below the surface. This cycle was likely to repeat many times. Death from above/below...
Dark Matter May Have Caused Earth’s Cataclysms, Mass Extinctions

Which hurts less?
a reply to: eisegesis
Sigh, the next mass scare move.
CO2 linked global warming is dead in the water.
We need the next 'what if?'
OA (ocean acidification) is the next boogie man alert. Not that there isn't a whole bunch of crap being dumped into the oceans besides our 'too low' CO2 levels.....
Sigh, the next mass scare move.
CO2 linked global warming is dead in the water.
We need the next 'what if?'
OA (ocean acidification) is the next boogie man alert. Not that there isn't a whole bunch of crap being dumped into the oceans besides our 'too low' CO2 levels.....
edit on 12-4-2015 by nwtrucker because: keyboard dysleksia
maybe it has something to do with the 2 piece asteroid that hit Australia. its said to have happened around 300 million years ago. i would think the
largest asteroid impact ever would be the catalyst for a mass extinction.
CO2 had very little to do with the Permian–Triassic extinction event.
CO2 was about 3000 ppm.
But you had high methane releases along with toxic levels of hydrogen sulfide.
plus a lot of Sulfur dioxide that is a lot worse at increasing acidity of the oceans.
Where was also low levels of O2 less then half of the levels now. around 10%
en.wikipedia.org...
This story is just a another scare story from the AGW people and has few real facts behind it and a lot of BS.
CO2 was about 3000 ppm.
But you had high methane releases along with toxic levels of hydrogen sulfide.
plus a lot of Sulfur dioxide that is a lot worse at increasing acidity of the oceans.
Where was also low levels of O2 less then half of the levels now. around 10%
en.wikipedia.org...
This story is just a another scare story from the AGW people and has few real facts behind it and a lot of BS.
edit on 12-4-2015 by ANNED
because: (no reason given)
Wonder if the next extinction will be driven by radioactive waters...aka Fukushima?
Can they terraform the earth if things get bad? I need to do some investigation on the subject.
originally posted by: ANNED
CO2 had very little to do with the Permian–Triassic extinction event.
CO2 was about 3000 ppm.
But you had high methane releases along with toxic levels of hydrogen sulfide.
plus a lot of Sulfur dioxide that is a lot worse at increasing acidity of the oceans.
Where was also low levels of O2 less then half of the levels now. around 10%
en.wikipedia.org...
This story is just a another scare story from the AGW people and has few real facts behind it and a lot of BS.
So to refute a brand new publication with new information, you cite Wikipedia - old information.
Even despite said old information that says this:
Suggested mechanisms for the latter include one or more large bolide impact events, massive volcanism, coal or gas fires and explosions from the Siberian Traps,and a runaway greenhouse effect triggered by sudden release of methane from the sea floor due to methane clathrate dissociation or methane-producing microbes known as methanogens; possible contributing gradual changes include sea-level change, increasing anoxia, increasing aridity, and a shift in ocean circulation driven by climate change.
You seem to dismiss ocean acidification - especially CO2 caused - when said Wikipedia article also says this:
The extinction primarily affected organisms with calcium carbonate skeletons, especially those reliant on stable CO2 levels to produce their skeletons, for the increase in atmospheric CO2 led to ocean acidification.
A similar text was introduced to this article all the way back in May 2010:
In addition, an increase in CO2 concentration leads to ocean acidification, consistent with the preferential extinction of heavilyt calcified taxa and signals in the rock record that suggest a more acidic ocean.
So, it's not a brand new idea. Suppose the 2-3000ppm CO2 level (as you suggest) had little to do with the acidification of the ocean then. Does that change the idea that acidification of the ocean caused a mass extinction? Isn't the ocean becoming more acidic now and isn't that some cause for worry?
new topics
-
They Know
Aliens and UFOs: 2 minutes ago -
Drones (QUESTION) TERMINATOR (QUESTION)
General Chit Chat: 1 hours ago -
Canada Banning more Shovels
General Chit Chat: 5 hours ago -
A priest who sexually assaulted a sleeping man on a train has been jailed for 16 months.
Social Issues and Civil Unrest: 10 hours ago -
The goal of UFO's/ fallen angels doesn't need to be questioned - It can be discerned
Aliens and UFOs: 10 hours ago
top topics
-
Jan 6th truth is starting to leak out.
US Political Madness: 17 hours ago, 23 flags -
Biden pardons 39 and commutes 1500 sentences…
Mainstream News: 16 hours ago, 8 flags -
The goal of UFO's/ fallen angels doesn't need to be questioned - It can be discerned
Aliens and UFOs: 10 hours ago, 5 flags -
Canada Banning more Shovels
General Chit Chat: 5 hours ago, 5 flags -
A priest who sexually assaulted a sleeping man on a train has been jailed for 16 months.
Social Issues and Civil Unrest: 10 hours ago, 2 flags -
Drones (QUESTION) TERMINATOR (QUESTION)
General Chit Chat: 1 hours ago, 0 flags -
They Know
Aliens and UFOs: 2 minutes ago, 0 flags
active topics
-
They Know
Aliens and UFOs • 0 • : ChaoticOrder -
The goal of UFO's/ fallen angels doesn't need to be questioned - It can be discerned
Aliens and UFOs • 9 • : onestonemonkey -
ILLUMINATION – Reverse Perception Of Cyclic Probability – CEO ASSASSINATION
Secret Societies • 26 • : Compendium -
Drones everywhere in New Jersey
Aliens and UFOs • 94 • : 38181 -
-@TH3WH17ERABB17- -Q- ---TIME TO SHOW THE WORLD--- -Part- --44--
Dissecting Disinformation • 3652 • : fringeofthefringe -
Canada Banning more Shovels
General Chit Chat • 2 • : chiefsmom -
Magic Vaporizing Ray Gun Claim - More Proof You Can't Believe Anything Hamas Says
War On Terrorism • 17 • : andy06shake -
Drones (QUESTION) TERMINATOR (QUESTION)
General Chit Chat • 2 • : BeyondKnowledge3 -
The Acronym Game .. Pt.4
General Chit Chat • 1011 • : JJproductions -
Jan 6th truth is starting to leak out.
US Political Madness • 21 • : network dude
11
