It looks like you're using an Ad Blocker.
Please white-list or disable AboveTopSecret.com in your ad-blocking tool.
Thank you.
Some features of ATS will be disabled while you continue to use an ad-blocker.
share:
originally posted by: Krazysh0t
originally posted by: WarminIndy
See the circular reasoning?
Darwinism is not true -> we have discovered more since Darwinism -> evolution is true because Darwin told us about it -> Darwinism is not true
If the whole premise of Darwinism was faulty, then anything built on it is faulty, yet somehow Darwinism is defended. Circular reasoning.
How many times does it have to be explained to you that modern evolutionary theory is built on Darwinian evolution? Darwinian evolution isn't 100% wrong, Darwin got the basic gist of how it works, he just didn't have all the available evidence that we do today and detailed an incomplete picture. The reason Darwinian evolution doesn't enter into modern evolutionary debates is because of this reason. That is like trying to say that because a Model T car cannot reach the speed of 120 miles per hour, a modern day race car is unable to do it. It is absurd and a VERY poor example of a circular reasoning. You want a GOOD example of circular reasoning?
How do we know the bible is true? It is the divine inspired word of god
How do we know that the bible is the divine inspired word of god? The bible says so.
As for the rest of your fallacies. Who cares? They don't pertain to evolution being true or not. I mean they are certainly valid fallacies, but they are irrelevant to the discussion because they neither prove nor disprove evolution. Though going by your tendency to embellish or conflate details, as can be seen from your example about peter vlar's work, I'd wager that these fallacies didn't work out the way you are describing them in this thread.
So now what? Do you continue in the fallacies during arguments?
That's the point of the whole discussion, because the fallacies are now pop culture, so how will you convince pop culture that the next scientific theory is valid if they hold on to the last one?
You still assume this is against scientific methods. No, this is about how the interpretations are forced into pop culture.
a reply to: Krazysh0t
I got my balls busted by a lot of people because it wasnt in line with what most people thought about Neanderthals at that time but its pretty widely accepted now that just about everyone of Eurasian descent has some HNS DNA proving there was inbreeding. That level of genetic testing and replication wasnt available 16 years ago. Nothing was suppressed, victory goes to he who has enough data to validate the hypothesis, plain and simple.
I got my balls busted by a lot of people because it wasnt in line with what most people thought about Neanderthals at that time but its pretty widely accepted now that just about everyone of Eurasian descent has some HNS DNA proving there was inbreeding. That level of genetic testing and replication wasnt available 16 years ago. Nothing was suppressed, victory goes to he who has enough data to validate the hypothesis, plain and simple.
a reply to: WarminIndy
Pop culture has no baring on the scientific method. Scientists don't go read tumblr or facebook before seeing if they can publish a study. They just publish it and let their peers review it and retest their findings. It's a process that takes time and has been proven to work well.
You clearly don't understand either Darwinian evolution or modern evolutionary synthesis if you think that the latter can't be built off of the former. You also clearly don't understand science if you think that doing so is a circular argument. And you also don't understand how science is developed if you think that pop culture determines if a theory is true or not.
Pop culture has no baring on the scientific method. Scientists don't go read tumblr or facebook before seeing if they can publish a study. They just publish it and let their peers review it and retest their findings. It's a process that takes time and has been proven to work well.
You clearly don't understand either Darwinian evolution or modern evolutionary synthesis if you think that the latter can't be built off of the former. You also clearly don't understand science if you think that doing so is a circular argument. And you also don't understand how science is developed if you think that pop culture determines if a theory is true or not.
a reply to: peter vlar
Exactly, that's what I was saying this whole time. If the science and evidence backing it up is sound then it will eventually be accepted. No one changes their mind over night.
Exactly, that's what I was saying this whole time. If the science and evidence backing it up is sound then it will eventually be accepted. No one changes their mind over night.
originally posted by: WarminIndy
originally posted by: Krazysh0t
originally posted by: WarminIndy
See the circular reasoning?
Darwinism is not true -> we have discovered more since Darwinism -> evolution is true because Darwin told us about it -> Darwinism is not true
If the whole premise of Darwinism was faulty, then anything built on it is faulty, yet somehow Darwinism is defended. Circular reasoning.
How many times does it have to be explained to you that modern evolutionary theory is built on Darwinian evolution? Darwinian evolution isn't 100% wrong, Darwin got the basic gist of how it works, he just didn't have all the available evidence that we do today and detailed an incomplete picture. The reason Darwinian evolution doesn't enter into modern evolutionary debates is because of this reason. That is like trying to say that because a Model T car cannot reach the speed of 120 miles per hour, a modern day race car is unable to do it. It is absurd and a VERY poor example of a circular reasoning. You want a GOOD example of circular reasoning?
How do we know the bible is true? It is the divine inspired word of god
How do we know that the bible is the divine inspired word of god? The bible says so.
As for the rest of your fallacies. Who cares? They don't pertain to evolution being true or not. I mean they are certainly valid fallacies, but they are irrelevant to the discussion because they neither prove nor disprove evolution. Though going by your tendency to embellish or conflate details, as can be seen from your example about peter vlar's work, I'd wager that these fallacies didn't work out the way you are describing them in this thread.
So now what? Do you continue in the fallacies during arguments?
That's the point of the whole discussion, because the fallacies are now pop culture, so how will you convince pop culture that the next scientific theory is valid if they hold on to the last one?
You still assume this is against scientific methods. No, this is about how the interpretations are forced into pop culture.
because of someone who watched a youtube video right? someone was fed misinformation by a youtube video and you are asking how REAL scientists first filter between youtube poop and actual scientific evidence, then how they distribute the resulting data effectively in order to curb misinformation? is that what the question here is?
originally posted by: WarminIndy
Premises - it is assumed that all Christians are against science.
Faulty premise because there are scientists who are Christians.
I don't think anybody has claimed that in this thread. Folks are talking about biblical literalists aka Christian fundamentalists. Nobody said all Christians are against science. Many of them are, however, and proof is in the threads in this section created by them. Creationist refers to one who believes the story of genesis as a 6 day literal story, not just someone who believes intelligent design. They are 2 different things.
Inference - it is inferred that Christians are not educated, therefore stupid.
Faulty inference - many Christians are highly intellectual and educated.
I didn't see anybody claim this. This applies to fundamentalists only because they ignore valid science in favor of personal faith. I know tons of rational Christians that accept science. Even the pope accepts evolution.
faulty argumentum - The premise for Christianity is that God does exist. Which takes us back to the original logical fallacy. What makes this faulty is that not every Christian doctrine is understood. Christians also teach Christian charity because the founder of the religion who was historical made historical claims to be nice to your neighbors and yet all religions teach a Golden Rule. Even non-religious people accept the Golden Rule. So the ad ignoratum is that all Christians must be wrong about all of premise, even though part of the premise is shared among all people groups.
People don't say the premise doesn't exist. They say there is no objective evidence for god (regardless of which god) OR evidence to verify the extraordinary claims in the bible (or Quaran, etc). Understanding the concept of empathy doesn't prove god or suggest Christianity as a whole is true. And the premise of Christianity is that Jesus died for everybody's sins so they can get into heaven. The golden rule was one of the things he taught, but it isn't the only aspect of Christianity, nor is it the main thing. It's important, yes, but it's also relative, and nobody can prove whether something is literally "right" or "wrong". They can prove what causes suffering to others and avoid this behavior. If I believed in Scientology and also taught empathy and shared stories about morality would that make Scientology true?
Argumentum ad misericordiam - fallacy here because I don't think this one has been presented by either side.
Sorry, but I don't see anybody suggesting evolution or god is true out of pity.
Argumentum ad populum - this logical fallacy is that on this thread the claims have been made that religion is detrimental
Who is arguing that religion is detrimental because the majority believe that? I'd say the majority do not even believe that because the majority of the world is religious. Appeal to popularity means that you claim something is true because most folks believe it. IE modern pop music is the best music of all time because it sells the highest would be this fallacy.
Faulty ad populum - Religions have offered good things to society.
You need to brush up on your fallacies. This has nothing to do with ad populum.
See, we could go on. If there is to be true debate, then the faulty logic must be removed in order to discuss anything. I never said religious people were against science, that was a charge made against religious people.
None of the fallacies you listed apply to evolutionary science. Logic would state that if somebody refuses to accept science despite tons of tangible, verifiable, repeatable evidence that they are against that particular science.
Darwinism is not true -> we have discovered more since Darwinism -> evolution is true because Darwin told us about it -> Darwinism is not true
If the whole premise of Darwinism was faulty, then anything built on it is faulty, yet somehow Darwinism is defended. Circular reasoning.
The problem is that you are using the wrong terminology and faulty logic to discredit evolution. Biologists that work in the field today do not call it Darwinism. The official name for the theory is "Modern Evolutionary Synthesis" and you have presented nothing whatsoever to counter it. Nobody is saying that evolution is true because Darwin said it. They are saying that the evidence has been accumulating over the past 150 years and THAT is what proves evolution. The premise of Darwin's original hypothesis WAS NOT FAULTY. He just didn't have the same knowledge we have today on the subject so to attack the original hypothesis without referring to any of the modern evidence is a HUGE fallacy.
You do not seem to understand fallacies or circular reasoning. Evolution supporters are saying to look at the evidence today and argue with THAT, rather than change the subject every time you hear something you don't really like or agree with.
I'm pretty sure that non sequitur counts as a fallacy as well and you have used this one dozens of times.
edit on 9-9-2014 by Barcs because:
(no reason given)
a reply to: WarminIndy
I never said you implied my methodology was incorrect, it was just a statement of fact, not an Indictment of you in any way.
As far as Eric Hedin is concerned, I don't think ID has any place in a physics class but that's just me. He was an untenured assistant professor so he technically didn't have job security in that sense but its irrelevant because I just looked at his current class schedule and he's still teaching there.
I never said you implied my methodology was incorrect, it was just a statement of fact, not an Indictment of you in any way.
As far as Eric Hedin is concerned, I don't think ID has any place in a physics class but that's just me. He was an untenured assistant professor so he technically didn't have job security in that sense but its irrelevant because I just looked at his current class schedule and he's still teaching there.
a reply to: Krazysh0t
And that's how it should be. If you're making an extraordinary claim that's contrary to a current paradigm then you have to be prepared to show extraordinary evidence to support your thesis. All I showed was extraordinary bravado and arrogance. Doesn't mean I was wrong, it just means I wasn't able to back my play at the time. It happens and if I choose to go continue that line of work in the future it will be much easier to do so with recent technological improvements as well as the current leanings regarding HNS. I was a little early for the show that's all. Things always have a way of working their way to the surface if its actually correct.
And that's how it should be. If you're making an extraordinary claim that's contrary to a current paradigm then you have to be prepared to show extraordinary evidence to support your thesis. All I showed was extraordinary bravado and arrogance. Doesn't mean I was wrong, it just means I wasn't able to back my play at the time. It happens and if I choose to go continue that line of work in the future it will be much easier to do so with recent technological improvements as well as the current leanings regarding HNS. I was a little early for the show that's all. Things always have a way of working their way to the surface if its actually correct.
a reply to: peter vlar
Sounds like it's working as intended to me. You know the saying "extraordinary claims requires extraordinary evidence," should be extended to have this part added to it, "...but once the extraordinary evidence is provided, the claim becomes an ordinary claim." Just think EVERY scientific idea that we currently hold true in modern society was at one point an extraordinary claim. The extraordinary evidence was provided and now it just seems ordinary.
Sounds like it's working as intended to me. You know the saying "extraordinary claims requires extraordinary evidence," should be extended to have this part added to it, "...but once the extraordinary evidence is provided, the claim becomes an ordinary claim." Just think EVERY scientific idea that we currently hold true in modern society was at one point an extraordinary claim. The extraordinary evidence was provided and now it just seems ordinary.
a reply to: Barcs
No, actually I did not ever say I don't believe in evolution. That was the assumption. And I did say that I am not the literalist.
What I am objecting to is this...people don't allow the scientists who do use science and employ the scientific methods to even be heard in the first place. All of this jumping the gun isn't helpful.
What I DID say is that I believe in the possibility of an Intelligence that designed the natural world, including the process of evolution.
I DID question the theories of speciation. I asked that if an individual in a population does not mutate at the same rate, is that individual no longer a member of the species.
But I was told that speciation and evolution is observed in evolution for a population. I was wondering then how that is, considering that populations are made of individuals. If evolution occurs at the population level, then what processes are occurring that some individuals evolve further than others, within the same population group.
Either the whole population of individuals evolve at the same rate, hence speciation, or there are differences in mutations occurring that make the individuals not as evolved.
So what process is occurring for the entire population? When experiments have been done, they have stated that it shows that not all evolve in the same way, and not all evolve to the same degree.
That is what I was asking about human population groups, not all individuals have mutated at the same rate nor at the same degree, however, if evolution is observed, then it is for the entire population. Does a whole population group evolve at the same rate? The answer was no, according to some. So then if evolution is leading toward speciation, then entire population groups, even of humans, becomes a species. However, we cannot say that not all of them mutated in the same manner because of sexual selection.
Some species have no alpha characters, while some have them. The rest of the population in that species group then still sexually reproduce, without alpha characters. So sexual selection only works for parts of the population, not the entire population.
See, these were questions I was asking and then giving my thoughts on the questions.
No, actually I did not ever say I don't believe in evolution. That was the assumption. And I did say that I am not the literalist.
What I am objecting to is this...people don't allow the scientists who do use science and employ the scientific methods to even be heard in the first place. All of this jumping the gun isn't helpful.
What I DID say is that I believe in the possibility of an Intelligence that designed the natural world, including the process of evolution.
I DID question the theories of speciation. I asked that if an individual in a population does not mutate at the same rate, is that individual no longer a member of the species.
But I was told that speciation and evolution is observed in evolution for a population. I was wondering then how that is, considering that populations are made of individuals. If evolution occurs at the population level, then what processes are occurring that some individuals evolve further than others, within the same population group.
Either the whole population of individuals evolve at the same rate, hence speciation, or there are differences in mutations occurring that make the individuals not as evolved.
So what process is occurring for the entire population? When experiments have been done, they have stated that it shows that not all evolve in the same way, and not all evolve to the same degree.
That is what I was asking about human population groups, not all individuals have mutated at the same rate nor at the same degree, however, if evolution is observed, then it is for the entire population. Does a whole population group evolve at the same rate? The answer was no, according to some. So then if evolution is leading toward speciation, then entire population groups, even of humans, becomes a species. However, we cannot say that not all of them mutated in the same manner because of sexual selection.
Some species have no alpha characters, while some have them. The rest of the population in that species group then still sexually reproduce, without alpha characters. So sexual selection only works for parts of the population, not the entire population.
See, these were questions I was asking and then giving my thoughts on the questions.
originally posted by: WarminIndy
What I am objecting to is this...people don't allow the scientists who do use science and employ the scientific methods to even be heard in the first place. All of this jumping the gun isn't helpful.
I don't understand this point. Which scientists are you referring to and what scientific methods are being ignored? If you are referring to intelligent design, there aren't any scientific experiments that can confirm or deny it. It relies on numerous assumptions.
What I DID say is that I believe in the possibility of an Intelligence that designed the natural world, including the process of evolution.
I DID question the theories of speciation. I asked that if an individual in a population does not mutate at the same rate, is that individual no longer a member of the species.
But I was told that speciation and evolution is observed in evolution for a population. I was wondering then how that is, considering that populations are made of individuals. If evolution occurs at the population level, then what processes are occurring that some individuals evolve further than others, within the same population group.
Either the whole population of individuals evolve at the same rate, hence speciation, or there are differences in mutations occurring that make the individuals not as evolved.
I'm certainly not saying ID is impossible. I gave you multiple examples of how individual traits can become dominant in a population and those points were ignored. You are creating a false dilemma. Natural selection is what guides evolution. You can't just keep repeating this point without even attempting to address the counterpoints that I presented. Every individual is unique in some way. "Not as evolved" isn't a concept in evolution either. Maybe "not as adapted to given environment." The bottom line is that if a trait is beneficial and leads to more of those genes being passed down, more individuals will begin to carry that same gene in the population.
So what process is occurring for the entire population? When experiments have been done, they have stated that it shows that not all evolve in the same way, and not all evolve to the same degree.
Like I just mentioned, natural selection is what "guides" evolution, not strictly mutations. Even if only 1% of the population has a favorable trait, an environmental change could kill off or drive out all of the ones that do not, so the amount of individuals that have it is completely irrelevant. You can't ignore natural selection when it comes to evolution. Sexual selection is only a part of that. Sometimes it has to do with survival directly. Sometimes it has to do with defense from predators. Sometimes it has to do with competition for food sources. Sometimes it has to do with being able to more efficiently find food. Sometimes it has to do with being more attractive to the opposite sex. There are numerous factors involved, and it has no bearing on whether a population accumulates genetic mutations at the same rate. In a nut shell, it's about who passes down the most genes.
And just an FYI, the amount of mutations is virtually the same since mutations occur at conception, not during the creature's lifetime. The exact genes affected is the random part and the amount of mutations slightly varies per individual. If you respond to this post, please address these exact points so this conversation can progress instead of going in circles and don't even think about changing the subject or going off on an unrelated tangent.
edit on 10-9-2014 by Barcs because: (no reason given)
a reply to: Barcs
But you, are you an evolved member of the species group, or are you a highly adapted individual in the highly adapted species group?
Is the whole species group highly adapted? I am sure that not every individual in the Homo Sapien group is as adapted in the same respect.
You say natural selection is the guide, but I am sure you meant that as non-personal force, however since natural selection certainly then favors certain individuals, and then that's why certain traits are passed on. But what makes an individual favored to carry these traits?
In genetic expression, the recombination of genetic material causes individuals of the same family group to receive different genes. I mean at the chromosomal level, this is basically Mendelian genetics, but it is evident that you receive randomly different traits than siblings, and it is expressed.
However, if natural selection were the guide of this, then it is in essence my brown eyed siblings were favored for that and my blue eyed siblings were favored for that. And yet members of the same family with the same ancestors. So not all traits are passed to an individual.
And yet it is through the recombination that can determine someone's ancestral population, but even so, one sibling can express more of a particular population than the other.
For instance, highly admixed individuals show varying percentages of vastly different populations, but people that have low admixture remain majority of certain populations. But does the recombination lead to a more highly adaptable individual? This is the question that Darwin was proposing when he said "Favored Races".
The prevailing idea at that time was that some races had adapted better therefore were more highly evolved. Now we know through DNA and genetics, that all ethnic groups have certain percentages, the typical Croat might have similar percentages of Balkan, Neanderthal and slight East Asian, but on the other hand a typical Italian might have Germanic, Italian and Neanderthal. Those are just some typical population groups into an admixtured person.
But then, neither the Croat or the Italian are different species, they certainly are different population group with their own gene expressions. And with each new generation, new recombinations are added into the mix. Take for instance Ashkenazi Jews. They have a unique genetic signature because Ashkenazi was a bottlenecked population several times in history. You know an Ashkenazi Jew by their markers.
Has evolution made Ashkenazi Jews what they are today? Clearly as Ashkenazi was a bottlenecked at certain points and little outside DNA was introduced to the women, but the men that were Ashkenazi introduced their DNA throughout Europe, and certain European women converted, then what happened that Ashkenazi have a unique genetic marker?
Was it through random mutations? No, it was more or less deliberate.
I am not trying to lead into a political debate over Ashkenazi, only that Ashkenazi are one population group that has a unique signature, other groups that do are East Asian Han Chinese and Roma. But populations that are bottlenecked, which means cut off from surrounding populations and breed only within the same population, does that lead to higher adaptability or evolved differently?
For each successive generation, new information is added only through sexual reproduction. And the recombination of that genetic information is expressed differently for each individual. Of the millions of ancestors that you and I have, there is only so much room for certain markers to be expressed in our chromosomes, but out of those millions of ancestors, because of the certain markers, it still makes me an individual but not an individual of a specific ethnic group.
There is no linear recombination, unless you are bottlenecked. Because of recombination, then where is the evidence of any eukaryote from the eukaryotic population? It is not expressed in any Homo Sapien, and yet everything about us is the result of genetic expression.
However, I am 2.9% Neanderthal as well. There should then be certain genetic traits that have passed down to me that are Neanderthal and if certain traits are passed down and expressed, then we have a population of Homo Neanderthalis Sapien that is AMH and yet at the same time, the Africans populations have no Neanderthal percenatages and now there is Denisovan. Yet, both population groups today are called AMH while having two vastly different ancestral populations that were never part of the same ancestral origins to begin with.
In evolutionary terms, I have not lost Neanderthal traits, they were passed down, but Subsaharan African, that is only .1% and many people say anything less that 1% should be called "noise", I have not retained traits from.
Please, I am not making this racist, merely an observation of genetic expression among various populations. It then doesn't seem to me that mutations are just random or that natural selection is what guides, because of the vastly different genetic populations and yet your chromosomes can only hold so much information from your ancestors. If mutations are random, then it would be a totally random thing to have individuals in the same population group to be completely different than others in the same group.
But this is speciation, which is populations that share similarity. It doesn't seem to work that way when certain population groups have unique markers. Are they evolved or are they adapated? And if they are adapted, then to what purpose?
But you, are you an evolved member of the species group, or are you a highly adapted individual in the highly adapted species group?
Is the whole species group highly adapted? I am sure that not every individual in the Homo Sapien group is as adapted in the same respect.
You say natural selection is the guide, but I am sure you meant that as non-personal force, however since natural selection certainly then favors certain individuals, and then that's why certain traits are passed on. But what makes an individual favored to carry these traits?
In genetic expression, the recombination of genetic material causes individuals of the same family group to receive different genes. I mean at the chromosomal level, this is basically Mendelian genetics, but it is evident that you receive randomly different traits than siblings, and it is expressed.
However, if natural selection were the guide of this, then it is in essence my brown eyed siblings were favored for that and my blue eyed siblings were favored for that. And yet members of the same family with the same ancestors. So not all traits are passed to an individual.
And yet it is through the recombination that can determine someone's ancestral population, but even so, one sibling can express more of a particular population than the other.
For instance, highly admixed individuals show varying percentages of vastly different populations, but people that have low admixture remain majority of certain populations. But does the recombination lead to a more highly adaptable individual? This is the question that Darwin was proposing when he said "Favored Races".
The prevailing idea at that time was that some races had adapted better therefore were more highly evolved. Now we know through DNA and genetics, that all ethnic groups have certain percentages, the typical Croat might have similar percentages of Balkan, Neanderthal and slight East Asian, but on the other hand a typical Italian might have Germanic, Italian and Neanderthal. Those are just some typical population groups into an admixtured person.
But then, neither the Croat or the Italian are different species, they certainly are different population group with their own gene expressions. And with each new generation, new recombinations are added into the mix. Take for instance Ashkenazi Jews. They have a unique genetic signature because Ashkenazi was a bottlenecked population several times in history. You know an Ashkenazi Jew by their markers.
Has evolution made Ashkenazi Jews what they are today? Clearly as Ashkenazi was a bottlenecked at certain points and little outside DNA was introduced to the women, but the men that were Ashkenazi introduced their DNA throughout Europe, and certain European women converted, then what happened that Ashkenazi have a unique genetic marker?
Was it through random mutations? No, it was more or less deliberate.
I am not trying to lead into a political debate over Ashkenazi, only that Ashkenazi are one population group that has a unique signature, other groups that do are East Asian Han Chinese and Roma. But populations that are bottlenecked, which means cut off from surrounding populations and breed only within the same population, does that lead to higher adaptability or evolved differently?
For each successive generation, new information is added only through sexual reproduction. And the recombination of that genetic information is expressed differently for each individual. Of the millions of ancestors that you and I have, there is only so much room for certain markers to be expressed in our chromosomes, but out of those millions of ancestors, because of the certain markers, it still makes me an individual but not an individual of a specific ethnic group.
There is no linear recombination, unless you are bottlenecked. Because of recombination, then where is the evidence of any eukaryote from the eukaryotic population? It is not expressed in any Homo Sapien, and yet everything about us is the result of genetic expression.
However, I am 2.9% Neanderthal as well. There should then be certain genetic traits that have passed down to me that are Neanderthal and if certain traits are passed down and expressed, then we have a population of Homo Neanderthalis Sapien that is AMH and yet at the same time, the Africans populations have no Neanderthal percenatages and now there is Denisovan. Yet, both population groups today are called AMH while having two vastly different ancestral populations that were never part of the same ancestral origins to begin with.
In evolutionary terms, I have not lost Neanderthal traits, they were passed down, but Subsaharan African, that is only .1% and many people say anything less that 1% should be called "noise", I have not retained traits from.
Please, I am not making this racist, merely an observation of genetic expression among various populations. It then doesn't seem to me that mutations are just random or that natural selection is what guides, because of the vastly different genetic populations and yet your chromosomes can only hold so much information from your ancestors. If mutations are random, then it would be a totally random thing to have individuals in the same population group to be completely different than others in the same group.
But this is speciation, which is populations that share similarity. It doesn't seem to work that way when certain population groups have unique markers. Are they evolved or are they adapated? And if they are adapted, then to what purpose?
a reply to: WarminIndy
The majority of genetic mutations are neutral. This means that from one generation to the next there are not many noticeable changes. Every offspring is a combination of the 2 parents DNA. Every offspring has dozens to hundreds of genetic mutations. You will not see 2 drastically different people in the same population group, unless they bred outside of that group except in rare cases. Some genes are dominant and some are recessive. All traits are passed down, and the dominant genes are way more likely to show up on the offspring.
I'm really having difficulty understanding your points. Evolution = genetic mutations sorted by natural selection, so when you ask "Has evolution made Ashkenazi Jews what they are today?", the obvious answer is yes. You are talking about something that taken thousands upon thousands of generations. If these people bottle necked and then introduced their genes to the the rest of the world, that has nothing to do with anything. It is still selection, because women and men of different "races" chose to breed with them. Humans are a bit different from the rest of the animal kingdom as well because they don't survive in the wild anymore. You're really reaching with this.
Highly adapted is a relative term because the environment has been changing over the hundreds of thousands of years humans have been on the planet. A highly adapted species could go from hero to zero in a single big environmental change. I'd say neither statement is true. I'm a homo sapien a member of the dominant species on the planet right now. The worst adapted species could become the best and the best could become the worst. It's all relative. Evolution isn't linear, it's constant and it follows the environment.
What do you mean by species group? Are you talking about homo sapiens as a whole? Americans? Africans? Your question makes no sense. You seem to be talking about races of human. They aren't separate species, they were just isolated into different environments for long periods of time. This is why Africans are better adapted to Africa and Europeans are better adapted to Europe. Most of this doesn't apply to modern humans however, because of technology. Humans travel all over the world and live and breed all over the place, regardless of race.
There aren't as many isolated populations as there were before. Don't forget that prior to 10,000 years ago, the world was in a glacial period for nearly 100,000 years. It was cold. This was when Neanderthals, Denisovans and others died out for the most part. During that time humans most likely lived in isolated places just trying to survive. This is how various races developed. They adapted to the environment that they were in over some 50,000 + years. Also it's important to understand that there was a bottleneck of humans that occurred a while back where the population dropped to around 10,000 individuals. This happened around 70,000 years ago.
Most of the time, it's just luck. Genetic mutations happen and the favorable ones are passed down because the others die out. There isn't a magic force that likes them, so they get blessed with the proper genes. At least not as far as we know. The environment on earth changes and thus the species do as well.
It does not always and that's not what Darwin meant by favored races. It was about surviving environmental changes, not being "highly adapted." Survival of the fittest. The level of fitness is determined by the environment in which they live. Race is more meant as the term "species"
In every cell in our bodies. A eukaryote is simply a cell that contains a nucleus and to go from talking about Jewish people to eukaryotes is a bit ridiculous. Humans (jews, africans, europeans, asians, etc) have been evolving for 200,000 years. The first Eukaryotes evolved 2 billion years ago. You are comparing apples to oranges. Obviously the changes in just 200,000 years would be nothing in comparison with 2 billion years.
No it wouldn't. I explained it above. Most mutations are neutral, although sometimes you do have individual that vary greatly from the rest. You aren't going to have 2 drastically different individuals just because they have recessive genes from older species that are not expressed. Most mutations are random, meaning at conception the genetic code isn't copied exactly because it's a combination of the 2 parents. The random part is which genes are mutated and mutations are caused by numerous factors. Remember, life has been here something like 3.8 billion years. You can't over simplify it. It's not either random genes OR natural selection. It's both!
Speciation is when two groups are isolated long enough to lose the capability to breed together. It is how new species originate. Unique markers are irrelevant. These things change over time. Evolution is long term adaptation. It's not either or.
The majority of genetic mutations are neutral. This means that from one generation to the next there are not many noticeable changes. Every offspring is a combination of the 2 parents DNA. Every offspring has dozens to hundreds of genetic mutations. You will not see 2 drastically different people in the same population group, unless they bred outside of that group except in rare cases. Some genes are dominant and some are recessive. All traits are passed down, and the dominant genes are way more likely to show up on the offspring.
I'm really having difficulty understanding your points. Evolution = genetic mutations sorted by natural selection, so when you ask "Has evolution made Ashkenazi Jews what they are today?", the obvious answer is yes. You are talking about something that taken thousands upon thousands of generations. If these people bottle necked and then introduced their genes to the the rest of the world, that has nothing to do with anything. It is still selection, because women and men of different "races" chose to breed with them. Humans are a bit different from the rest of the animal kingdom as well because they don't survive in the wild anymore. You're really reaching with this.
But you, are you an evolved member of the species group, or are you a highly adapted individual in the highly adapted species group?
Highly adapted is a relative term because the environment has been changing over the hundreds of thousands of years humans have been on the planet. A highly adapted species could go from hero to zero in a single big environmental change. I'd say neither statement is true. I'm a homo sapien a member of the dominant species on the planet right now. The worst adapted species could become the best and the best could become the worst. It's all relative. Evolution isn't linear, it's constant and it follows the environment.
Is the whole species group highly adapted? I am sure that not every individual in the Homo Sapien group is as adapted in the same respect.
What do you mean by species group? Are you talking about homo sapiens as a whole? Americans? Africans? Your question makes no sense. You seem to be talking about races of human. They aren't separate species, they were just isolated into different environments for long periods of time. This is why Africans are better adapted to Africa and Europeans are better adapted to Europe. Most of this doesn't apply to modern humans however, because of technology. Humans travel all over the world and live and breed all over the place, regardless of race.
There aren't as many isolated populations as there were before. Don't forget that prior to 10,000 years ago, the world was in a glacial period for nearly 100,000 years. It was cold. This was when Neanderthals, Denisovans and others died out for the most part. During that time humans most likely lived in isolated places just trying to survive. This is how various races developed. They adapted to the environment that they were in over some 50,000 + years. Also it's important to understand that there was a bottleneck of humans that occurred a while back where the population dropped to around 10,000 individuals. This happened around 70,000 years ago.
natural selection certainly then favors certain individuals, and then that's why certain traits are passed on. But what makes an individual favored to carry these traits?
Most of the time, it's just luck. Genetic mutations happen and the favorable ones are passed down because the others die out. There isn't a magic force that likes them, so they get blessed with the proper genes. At least not as far as we know. The environment on earth changes and thus the species do as well.
But does the recombination lead to a more highly adaptable individual? This is the question that Darwin was proposing when he said "Favored Races".
It does not always and that's not what Darwin meant by favored races. It was about surviving environmental changes, not being "highly adapted." Survival of the fittest. The level of fitness is determined by the environment in which they live. Race is more meant as the term "species"
where is the evidence of any eukaryote from the eukaryotic population?
In every cell in our bodies. A eukaryote is simply a cell that contains a nucleus and to go from talking about Jewish people to eukaryotes is a bit ridiculous. Humans (jews, africans, europeans, asians, etc) have been evolving for 200,000 years. The first Eukaryotes evolved 2 billion years ago. You are comparing apples to oranges. Obviously the changes in just 200,000 years would be nothing in comparison with 2 billion years.
It then doesn't seem to me that mutations are just random or that natural selection is what guides, because of the vastly different genetic populations and yet your chromosomes can only hold so much information from your ancestors. If mutations are random, then it would be a totally random thing to have individuals in the same population group to be completely different than others in the same group.
No it wouldn't. I explained it above. Most mutations are neutral, although sometimes you do have individual that vary greatly from the rest. You aren't going to have 2 drastically different individuals just because they have recessive genes from older species that are not expressed. Most mutations are random, meaning at conception the genetic code isn't copied exactly because it's a combination of the 2 parents. The random part is which genes are mutated and mutations are caused by numerous factors. Remember, life has been here something like 3.8 billion years. You can't over simplify it. It's not either random genes OR natural selection. It's both!
But this is speciation, which is populations that share similarity. It doesn't seem to work that way when certain population groups have unique markers. Are they evolved or are they adapated? And if they are adapted, then to what purpose?
Speciation is when two groups are isolated long enough to lose the capability to breed together. It is how new species originate. Unique markers are irrelevant. These things change over time. Evolution is long term adaptation. It's not either or.
edit on 10-9-2014 by Barcs because: (no reason given)
a reply to: Barcs
OK, I have to explain the word usage that I am trying to express...
OK, this is given in human terms..so in human terms this is the expression I am talking about. But the biological definition is this...
OK, belonging to the same species. There can be two or more species in the same geographic location. We all keep pets, so they are in the same location, but as different species.
And if a population has individuals living in the same place at the same time, then humans, which are a species, do not live in the same place at the same time, and yet not all mammals can do that.
Lions live in Africa, kangaroos live in Australia, except for zoos in Stockholm or Berlin. But naturally, those animals typically remain in their own geographic regions. Therefore, they are adapted to live in their environments, yes?
But humans can live anywhere, reasonably, except for in water. They can live in Arctic or Antarctic regions only with the ability themselves to adapt, but never naturally.
And that's what I am trying to say, if a human population can live naturally anywhere, except those places, then why have humans not reverted to being able to live in the water? We don't see Polynesians that have devolved or reverted to being able to live in water.
So my point was, given that species are considered populations, and species are subject to evolution, then it can only occur at the individual level, even though evolution is counted at the population level. So if a group of people are naturally adapted through random means, then human population groups must have been adapted for specific geographic regions, individually.
And if this happened, was it because of environment or did it happened before they encountered the new environments?
If an adaptability is random and not preordered, then this cannot be true...Human Biological Adaptation
And yet human population groups are capable of living in Tropical zones and still remain a particular skin color. Hence, Richard Dawkins is a white European that grew up in Africa. So who in his family was adapted for him to remain with very little change that Richard Dawkins remains as Caucasian, living in the very zone that nature selects for people to have dark skin tones?
This is part of the problem with the words, "nature selects". If it is random, then it is not selection. If it is selection, then it can't be a random process.
That means that nature itself has specifically chosen some individuals to live in certain regions, naturally. But that is not true as all humans can live anywhere, despite selection and adaptation.
OK, then if this was selection, to prevent some individuals to get cancer, then anywhere else in the world there should be a different level of radiation.
From Global Ground Radiation
And here
But it also depends upon other variables
As different areas receive a different amount of sunlight for different time periods
How does this relate to randomness or selection? Evolution in particular groups must have different rates of evolutions, however, the current thought is that since we are all the same species, then evolution should have been constant across the entire species, but it can't be if radiation contributes to evolution selection.
So did the evolution of certain groups occur in one particular locations or did it occur after certain individuals went to another location?
OK, I have to explain the word usage that I am trying to express...
pop·u·la·tion
ˌpäpyəˈlāSHən/Submit
noun
all the inhabitants of a particular town, area, or country.
"the island has a population of about 78,000"
synonyms: inhabitants, residents, people, citizens, citizenry, public, community, populace, society, body politic, natives, occupants; formaldenizens
"a new social agenda for the population of these emerging nations"
a particular section, group, or type of people or animals living in an area or country.
"the country's immigrant population"
the specified extent or degree to which an area is or has been populated.
"areas of sparse population"
OK, this is given in human terms..so in human terms this is the expression I am talking about. But the biological definition is this...
In biology, populations are groups of individuals belonging to the same species that live in the same region at the same time. Population density is a measure of the number of organisms that make up a population in a defined area.
OK, belonging to the same species. There can be two or more species in the same geographic location. We all keep pets, so they are in the same location, but as different species.
And if a population has individuals living in the same place at the same time, then humans, which are a species, do not live in the same place at the same time, and yet not all mammals can do that.
Lions live in Africa, kangaroos live in Australia, except for zoos in Stockholm or Berlin. But naturally, those animals typically remain in their own geographic regions. Therefore, they are adapted to live in their environments, yes?
But humans can live anywhere, reasonably, except for in water. They can live in Arctic or Antarctic regions only with the ability themselves to adapt, but never naturally.
And that's what I am trying to say, if a human population can live naturally anywhere, except those places, then why have humans not reverted to being able to live in the water? We don't see Polynesians that have devolved or reverted to being able to live in water.
So my point was, given that species are considered populations, and species are subject to evolution, then it can only occur at the individual level, even though evolution is counted at the population level. So if a group of people are naturally adapted through random means, then human population groups must have been adapted for specific geographic regions, individually.
And if this happened, was it because of environment or did it happened before they encountered the new environments?
If an adaptability is random and not preordered, then this cannot be true...Human Biological Adaptation
Nature has selected for people with darker skin in tropical latitudes, especially in nonforested regions, where ultraviolet radiation from the sun is usually the most intense.
And yet human population groups are capable of living in Tropical zones and still remain a particular skin color. Hence, Richard Dawkins is a white European that grew up in Africa. So who in his family was adapted for him to remain with very little change that Richard Dawkins remains as Caucasian, living in the very zone that nature selects for people to have dark skin tones?
This is part of the problem with the words, "nature selects". If it is random, then it is not selection. If it is selection, then it can't be a random process.
That means that nature itself has specifically chosen some individuals to live in certain regions, naturally. But that is not true as all humans can live anywhere, despite selection and adaptation.
By doing this, it helps to prevent sunburn damage that could result in DNA changes and, subsequently, several kinds of malignant skin cancers.
OK, then if this was selection, to prevent some individuals to get cancer, then anywhere else in the world there should be a different level of radiation.
From Global Ground Radiation
e. Since the Sun radiance varies to some extent over short and long periods (Fröhlich 1991), the solar constant does not remain steady over time. There is a variation of about ± 1 Wm-2 around the mean solar constant during a typical Sun cycle of 11 years (Gueymard and Myers 2008)
And here
Terrestrial Spectra
The spectrum of the solar radiation at the earth's surface has several components (see Fig. 2). Direct radiation comes straight from the sun, diffuse radiation is scattered from the sky and from the surroundings. Additional radiation reflected from the surroundings (ground or sea) depends on the local "albedo." The total ground radiation is called the global radiation. The direction of the target surface must be defined for global irradiance. For direct radiation the target surface faces the incoming beam.
But it also depends upon other variables
The Changing Terrestrial Solar Spectrum
Absorption and scattering levels change as the constituents of the atmosphere change. Clouds are the most familiar example of change; clouds can block most of the direct radiation. Seasonal variations and trends in ozone layer thickness have an important effect on terrestrial ultraviolet level.
As different areas receive a different amount of sunlight for different time periods
Standard Spectra
Solar radiation reaching the earth's surface varies significantly with location, atmospheric conditions including cloud cover, aerosol content, and ozone layer condition, and time of day, earth/sun distance, solar rotation and activity. Since the solar spectra depend on so many variables, standard spectra have been developed to provide a basis for theoretical evaluation of the effects of solar radiation and as a basis for simulator design. These standard spectra start from a simplified (i.e. lower resolution) version of the measured extraterrestrial spectra, and use sophisticated models for the effects of the atmosphere to calculate terrestrial spectra.
How does this relate to randomness or selection? Evolution in particular groups must have different rates of evolutions, however, the current thought is that since we are all the same species, then evolution should have been constant across the entire species, but it can't be if radiation contributes to evolution selection.
So did the evolution of certain groups occur in one particular locations or did it occur after certain individuals went to another location?
originally posted by: WarminIndy
Lions live in Africa, kangaroos live in Australia, except for zoos in Stockholm or Berlin. But naturally, those animals typically remain in their own geographic regions. Therefore, they are adapted to live in their environments, yes?
But humans can live anywhere, reasonably, except for in water. They can live in Arctic or Antarctic regions only with the ability themselves to adapt, but never naturally.
And that's what I am trying to say, if a human population can live naturally anywhere, except those places, then why have humans not reverted to being able to live in the water? We don't see Polynesians that have devolved or reverted to being able to live in water.
theres no such thing as Devolving. Evolution is the sum of genetic changes over time, that all. There is no forward or backwards or most evolved or less evolved.
So my point was, given that species are considered populations, and species are subject to evolution, then it can only occur at the individual level, even though evolution is counted at the population level. So if a group of people are naturally adapted through random means, then human population groups must have been adapted for specific geographic regions, individually.
that still doesn't put it at an individual level. You're over thinking it and trying to make it more complicated than it is.
And yet human population groups are capable of living in Tropical zones and still remain a particular skin color. Hence, Richard Dawkins is a white European that grew up in Africa. So who in his family was adapted for him to remain with very little change that Richard Dawkins remains as Caucasian, living in the very zone that nature selects for people to have dark skin tones?
I'm sorry but that's so far outside the bounds of any biological or anthropological theory or hypothesis that it's almost insane. Just because he can survive in that environment with modern technology doesn't mean he would have thrived in it let alone been able to pass on his genes if he were to have spent the rest of his days their. This is some serious mental gymnastics to get this to appear logical, I'm sorry.
So did the evolution of certain groups occur in one particular locations or did it occur after certain individuals went to another location?
Both. Anatomically modern humans evolved in East Africa, the oldest confirmed remains are from Ethiopia and are over 160,000 years old. The initial adaptation is for that climate. As humans moved out of Africa and into other ecological niches, they slowly adapted to those as well.
originally posted by: peter vlar
originally posted by: WarminIndy
Lions live in Africa, kangaroos live in Australia, except for zoos in Stockholm or Berlin. But naturally, those animals typically remain in their own geographic regions. Therefore, they are adapted to live in their environments, yes?
But humans can live anywhere, reasonably, except for in water. They can live in Arctic or Antarctic regions only with the ability themselves to adapt, but never naturally.
And that's what I am trying to say, if a human population can live naturally anywhere, except those places, then why have humans not reverted to being able to live in the water? We don't see Polynesians that have devolved or reverted to being able to live in water.
theres no such thing as Devolving. Evolution is the sum of genetic changes over time, that all. There is no forward or backwards or most evolved or less evolved.
So my point was, given that species are considered populations, and species are subject to evolution, then it can only occur at the individual level, even though evolution is counted at the population level. So if a group of people are naturally adapted through random means, then human population groups must have been adapted for specific geographic regions, individually.
that still doesn't put it at an individual level. You're over thinking it and trying to make it more complicated than it is.
And yet human population groups are capable of living in Tropical zones and still remain a particular skin color. Hence, Richard Dawkins is a white European that grew up in Africa. So who in his family was adapted for him to remain with very little change that Richard Dawkins remains as Caucasian, living in the very zone that nature selects for people to have dark skin tones?
I'm sorry but that's so far outside the bounds of any biological or anthropological theory or hypothesis that it's almost insane. Just because he can survive in that environment with modern technology doesn't mean he would have thrived in it let alone been able to pass on his genes if he were to have spent the rest of his days their. This is some serious mental gymnastics to get this to appear logical, I'm sorry.
So did the evolution of certain groups occur in one particular locations or did it occur after certain individuals went to another location?
Both. Anatomically modern humans evolved in East Africa, the oldest confirmed remains are from Ethiopia and are over 160,000 years old. The initial adaptation is for that climate. As humans moved out of Africa and into other ecological niches, they slowly adapted to those as well.
This is a game she plays. My suggestion is to not feed into it.
originally posted by: Tangerine
originally posted by: peter vlar
originally posted by: WarminIndy
This is a game she plays. My suggestion is to not feed into it.
Really? Because I disagree with you, that means I am playing a game? Please go ad hominim elsewhere.
Peter Vlar is a scientist and Peter Vlar is quite capable of having a conversation with me and yet not one time have I interjected Intelligent Design into this phase of conversation.
Now if you don't mind, I will continue on, because these are questions people should be asking. You might disagree with me, but ultimately you will have to accept that because someone disagrees does not mean they are playing a game.
a reply to: peter vlar
Thank you for the science discussion. I recognize that this is your field, but as a layperson, I still have the right to ask questions.
Now, about mtDNA haplotypes, mine is T2b, so that's where I focus most of my energy at, understanding the T clade and my subclade T2b.
This particular abstract says says
I mentioned bottlenecked populations.
OK for understanding T2b, we have to know the history of the population in question, so I will focus on T2b, if that is ok.
So if there is a decreased speed of adaptation, then my statement that certain populations do not adapt as the same rate still holds.
I asked in the context of recombination and here is the what the author says
I made the statement with the understanding that there are very highly admixed people groups as well as low admixture, the Ashkenazi were simply set as an example of a low admixed, bottlenecked population group. So it could be assumed then by the literature that this group had a lower speed of adaptation. This is what I simply said and nothing was implied in that. I also mentioned Han Chinese and Roma, as well as Native American. Currently there are only four accepted mtDNA haplotypes for Native Americans.
I wanted to remain with T and T2b for now.
From NCBI
What does it mean, different evolutionary pattern for the three primary mutations? There are recent, and yet there is also ancient mutations, in an evolutionary sense, meaning that J is unique because there are specific mutations. Something is going on with the women.
Another article from NCBI states this.
OK J and T have no intermediates, but it shows that J and T both arose in the Levant.
This is my ancestresses lineage, so I feel I should be able to discuss this.
How does T2b get into Europe, before T2b arose?
T2b is indigenous to the Levant. While it says that
OK, as it says here, they were not the AMH, but they come from a more ancient population.
They arose at the same time R did, in the Levant, so R can not be ancestral if they arose at the same time. But their clade is indigenous
OK, what have we got going on here? That means that T2b is an indigenous European population, and that it was not bottlenecked, meaning that it had a different and accelerated evolutionary process. Therefore, not all populations of human groups can evolve at the same rate and speed, that means some populations reach speciation before others.
Would this not be true? But as genetics for evolution have been based primarily before on male individuals within the Homo Species.
TBC...
Thank you for the science discussion. I recognize that this is your field, but as a layperson, I still have the right to ask questions.
Now, about mtDNA haplotypes, mine is T2b, so that's where I focus most of my energy at, understanding the T clade and my subclade T2b.
This particular abstract says says
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) has been a marker of choice for reconstructing historical patterns of population demography, admixture, biogeography and speciation. However, it has recently been suggested that the pervasive nature of direct and indirect selection on this molecule renders any conclusion derived from it ambiguous
I mentioned bottlenecked populations.
The study of evolution frequently requires understanding the history of the population, species or clade under study. In population genetics, a recent history of population bottlenecks may restrict genetic variation and thus constrain the speed of adaptation. In examining diversification over space, we need to have detailed knowledge of the different populations' histories of colonization and the gene flow between them
OK for understanding T2b, we have to know the history of the population in question, so I will focus on T2b, if that is ok.
So if there is a decreased speed of adaptation, then my statement that certain populations do not adapt as the same rate still holds.
I asked in the context of recombination and here is the what the author says
Thirdly, as an area of at least low recombination, the whole molecule can be assumed to have the same genealogical history.
I made the statement with the understanding that there are very highly admixed people groups as well as low admixture, the Ashkenazi were simply set as an example of a low admixed, bottlenecked population group. So it could be assumed then by the literature that this group had a lower speed of adaptation. This is what I simply said and nothing was implied in that. I also mentioned Han Chinese and Roma, as well as Native American. Currently there are only four accepted mtDNA haplotypes for Native Americans.
I wanted to remain with T and T2b for now.
From NCBI
This analysis shows that the putative secondary/intermediate LHON mutations 4216, 4917, 13708, 15257, and 15812 are ancient polymorphisms, are associated in specific combinations, and define two common Caucasoid-specific haplotype groupings (haplogroups J and T). On the contrary, the same analysis shows that the primary mutations 11778, 3460, and 14484 are recent and are due to multiple mutational events. However, phylogenetic analysis also reveals a different evolutionary pattern for the three primary mutations. The 3460 mutations are distributed randomly along the phylogenetic trees, without any preferential association with the nine haplogroups (H, I, J, K, T, U, V, W, and X) that characterize European populations, whereas the 11778 and 14484 mutations show a strong preferential association with haplogroup J. This finding suggests that one ancient combination of haplogroup J-specific mutations increases both the penetrance of the two primary mutations 11778 and 14484 and the risk of disease expression.
What does it mean, different evolutionary pattern for the three primary mutations? There are recent, and yet there is also ancient mutations, in an evolutionary sense, meaning that J is unique because there are specific mutations. Something is going on with the women.
Another article from NCBI states this.
The JT tree (outlined in Figure 1; see Figures S1 and S2 for details) confirms the presence of two main phylogenetic clusters, J and T, with no intermediates. The ML age estimates suggest that JT arose ∼58 ka ago, probably before the settlement of the Fertile Crescent according to current evidence, and that J and T diverged within the timeframe of settlement in the Fertile Crescent, ∼40 ka (with ML; ∼35 ka with ρ) and ∼30 ka ago, respectively (Table 1). Fragments of both J and T now extend well beyond their core Near Eastern and European range into North Africa, the Indian subcontinent, and central Asia
OK J and T have no intermediates, but it shows that J and T both arose in the Levant.
Like haplogroup J, haplogroup T falls into two distinct subclades, T1 and T2. However, the structure of these subclades is more complex than that of the five nested subclades found in J. Both T1 and T2 include several paraphyletic lineages, and whereas T1 falls into just two nested subclades, T2 displays at least nine, although a single one, T2b, encompasses about half of T2 among Europeans.
This is my ancestresses lineage, so I feel I should be able to discuss this.
The early presence of T2 in Europe (even with the assumption that it arose in the Near East) suggests that ancestors of T2b might have been present in Europe well before the age of T2b itself, at any time back to the LGM, although T2b seems to have been dispersed within Europe during the early Neolithic period.
How does T2b get into Europe, before T2b arose?
Several minor T2 subclades, such as T2g, T2h, and T2i, are found in both Europe and the Near East and remain enigmatic. Additional subclades, represented by only two complete mtDNAs each, along with many more paraphyletic members of T2, have so far been seen almost exclusively in Europe and date collectively (as a paragroup) to the Late Glacial period.
T2b is indigenous to the Levant. While it says that
Our analysis confirms that haplogroups J and T and their major subclades (J1 and J2, T1 and T2) most likely arose in the Near East between the time of first settlement by modern humans and the LGM
OK, as it says here, they were not the AMH, but they come from a more ancient population.
It seems plausible to regard JT and U as belonging to members of the same early human group, ancestral to both Near Easterners and Europeans.
They arose at the same time R did, in the Levant, so R can not be ancestral if they arose at the same time. But their clade is indigenous
Indeed, the major T2 lineage, T2b, although displaying a star-like pattern dating to ∼10 ka ago, suggesting an expansion across Europe at the time of the early Neolithic period, may well have arisen indigenously within Europe from a T2 ancestor.
OK, what have we got going on here? That means that T2b is an indigenous European population, and that it was not bottlenecked, meaning that it had a different and accelerated evolutionary process. Therefore, not all populations of human groups can evolve at the same rate and speed, that means some populations reach speciation before others.
Would this not be true? But as genetics for evolution have been based primarily before on male individuals within the Homo Species.
It was recognized at the outset that mtDNA was strictly a marker for historical processes in females; should male and female history differ in a species, then this marker would not reflect the history of the species as a whole but that of the female portion.
TBC...
a reply to: Barcs
You and the OP are speaking different languages. You are defining a Christian as someone who identifies themselves as such. To the OP, only Christian fundamentalists are 'Christians'.
I don't think anybody has claimed that in this thread. Folks are talking about biblical literalists aka Christian fundamentalists. Nobody said all Christians are against science.
You and the OP are speaking different languages. You are defining a Christian as someone who identifies themselves as such. To the OP, only Christian fundamentalists are 'Christians'.
originally posted by: WarminIndy
a reply to: peter vlar
Thank you for the science discussion. I recognize that this is your field, but as a layperson, I still have the right to ask questions.
Absolutely, I'm in no way saying you can't or shouldn't ask questions. I don't agree that your playing a game but I do think your rather far off the beaten path and will attempt to point you in the right direction if I am able.
Now, about mtDNA haplotypes, mine is T2b, so that's where I focus most of my energy at, understanding the T clade and my subclade T2b.
I mentioned bottlenecked populations.
OK for understanding T2b, we have to know the history of the population in question, so I will focus on T2b, if that is ok.
So if there is a decreased speed of adaptation, then my statement that certain populations do not adapt as the same rate still holds.
There's no argument that adaptation or mutation rates lack uniformity. its not possible for these processes to be uniform as the dispersal of HSS and consequently our genomes, was not uniform either chronologically or geographically and in many instances there are back migrations into older populations.
I asked in the context of recombination and here is the what the author says
Thirdly, as an area of at least low recombination, the whole molecule can be assumed to have the same genealogical history.
I made the statement with the understanding that there are very highly admixed people groups as well as low admixture, the Ashkenazi were simply set as an example of a low admixed, bottlenecked population group. So it could be assumed then by the literature that this group had a lower speed of adaptation. This is what I simply said and nothing was implied in that. I also mentioned Han Chinese and Roma, as well as Native American. Currently there are only four accepted mtDNA haplotypes for Native Americans.
I wanted to remain with T and T2b for now.
From NCBI
This analysis shows that the putative secondary/intermediate LHON mutations 4216, 4917, 13708, 15257, and 15812 are ancient polymorphisms, are associated in specific combinations, and define two common Caucasoid-specific haplotype groupings (haplogroups J and T). On the contrary, the same analysis shows that the primary mutations 11778, 3460, and 14484 are recent and are due to multiple mutational events. However, phylogenetic analysis also reveals a different evolutionary pattern for the three primary mutations. The 3460 mutations are distributed randomly along the phylogenetic trees, without any preferential association with the nine haplogroups (H, I, J, K, T, U, V, W, and X) that characterize European populations, whereas the 11778 and 14484 mutations show a strong preferential association with haplogroup J. This finding suggests that one ancient combination of haplogroup J-specific mutations increases both the penetrance of the two primary mutations 11778 and 14484 and the risk of disease expression.
What does it mean, different evolutionary pattern for the three primary mutations? There are recent, and yet there is also ancient mutations, in an evolutionary sense, meaning that J is unique because there are specific mutations. Something is going on with the women.
I think you're reading far too much into this analysis. You're basing this entirely off of mtDNA Haplogroups which as a whole, is really good at looking way back into our history and looking at populations migration patterns and where and when they picked up new genes or mutations. It can't however give you a complete picture and you would be better served looking at the Y dna haplogroups in my opinion. Obviously you've been doing a lot of research trying to find your own origins which is very commendable, I just think you're trying to paint tan entire picture off of less than whole information.
OK J and T have no intermediates, but it shows that J and T both arose in the Levant.
T yes and it's a bit more recent than J, approx. 25,000 BPE (+/- 5,000). Everything I've read however indicates a slightly more northern origin for J, in the Caucuses around 45,000 BPE It's a pretty well researched clade with a lot written about it so there is an enormous amount of information out there. I'm not sure what you mean by no intermediates, they are both descended from JT which arose in SW Asia 50,000 BPE When each arose and where is a matter of a random mutation so theres no need to be concerned with regard to chronology in this regard.
This is my ancestresses lineage, so I feel I should be able to discuss this.
nobody is trying to stop that, I'm still here discussing it aren't I?
How does T2b get into Europe, before T2b arose?
That's not what it's saying, it's saying that the ancestors, that is people who would eventually inherit this gene, were there. The most likely route from Mesopotamia to Europe was across the Caspian and through the Balkans where it finally landed in Italy which has a fairly high percentage of people with this particular Haplogroup.
T2b is indigenous to the Levant. While it says that
Our analysis confirms that haplogroups J and T and their major subclades (J1 and J2, T1 and T2) most likely arose in the Near East between the time of first settlement by modern humans and the LGM
OK, as it says here, they were not the AMH, but they come from a more ancient population.
It seems plausible to regard JT and U as belonging to members of the same early human group, ancestral to both Near Easterners and Europeans.
Where exactly does it say not AMH? Did I miss something?
They arose at the same time R did, in the Levant, so R can not be ancestral if they arose at the same time. But their clade is indigenous
Indeed, the major T2 lineage, T2b, although displaying a star-like pattern dating to ∼10 ka ago, suggesting an expansion across Europe at the time of the early Neolithic period, may well have arisen indigenously within Europe from a T2 ancestor.
OK, what have we got going on here? That means that T2b is an indigenous European population, and that it was not bottlenecked, meaning that it had a different and accelerated evolutionary process. Therefore, not all populations of human groups can evolve at the same rate and speed, that means some populations reach speciation before others.
Would this not be true? But as genetics for evolution have been based primarily before on male individuals within the Homo Species.
It was recognized at the outset that mtDNA was strictly a marker for historical processes in females; should male and female history differ in a species, then this marker would not reflect the history of the species as a whole but that of the female portion.
TBC...
Sorry, I'm a little pressed for time right now so I've got to be quick about this. Perhaps this map will be able to help you visualize things a little differently. If not, I will try to explain more thoroughly when I come back to my PC. Sorry for the hit and run but something came up while I was trying to put my reply together and the screaming 6 year old takes precedence for now.
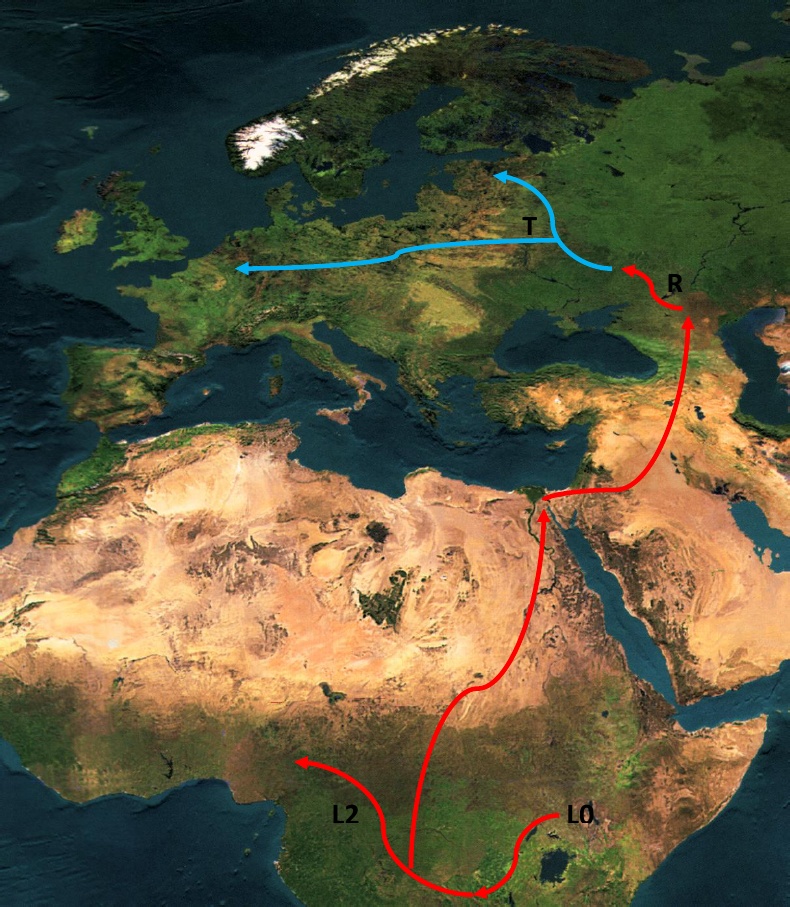
new topics
-
A family from Kansas with six children moved to the Moscow region
Other Current Events: 2 hours ago -
Revolution in advertising: the Russians launched a unique satellite
Science & Technology: 4 hours ago -
Echo & The Bunnymen - The Killing Moon!
Music: 7 hours ago -
I Guess Cloud Seeding Works
Fragile Earth: 9 hours ago -
Canadian Forces bow out and loose interest in UFO’s
Aliens and UFOs: 10 hours ago
top topics
-
The US Supreme Court Appears to Side With the January 6th 2021 Capitol Protestors.
Political Conspiracies: 13 hours ago, 20 flags -
That which the "news" never talks about; Truth about election fraud
Mainstream News: 14 hours ago, 15 flags -
I Guess Cloud Seeding Works
Fragile Earth: 9 hours ago, 9 flags -
Biden doesnt want the votes of "Death to America" chanters
US Political Madness: 15 hours ago, 9 flags -
Canadian Forces bow out and loose interest in UFO’s
Aliens and UFOs: 10 hours ago, 6 flags -
Joe Biden and Donald Trump are both traitors
2024 Elections: 17 hours ago, 4 flags -
Revolution in advertising: the Russians launched a unique satellite
Science & Technology: 4 hours ago, 3 flags -
A family from Kansas with six children moved to the Moscow region
Other Current Events: 2 hours ago, 2 flags -
Horizon Post office scandal
Regional Politics: 15 hours ago, 1 flags -
Echo & The Bunnymen - The Killing Moon!
Music: 7 hours ago, 1 flags
active topics
-
It has begun... Iran begins attack on Israel, launches tons of drones towards the country
World War Three • 809 • : Astrocometus -
Revolution in advertising: the Russians launched a unique satellite
Science & Technology • 29 • : Freeborn -
I'm new here. Avid conspiracy fan.
Introductions • 19 • : chiefsmom -
A family from Kansas with six children moved to the Moscow region
Other Current Events • 16 • : Kurokage -
I Guess Cloud Seeding Works
Fragile Earth • 9 • : Justoneman -
Mood Music Part VI
Music • 3047 • : TheWoker -
US and Israel Reportedly Conclude Most Hostages Still Held in Gaza Are Dead
War On Terrorism • 154 • : FlyersFan -
Running Through Idiot Protestors Who Block The Road
Rant • 80 • : TheWoker -
Putin Compares Himself to Jesus Promoting Traditional Values Against the Satanic West
Mainstream News • 72 • : purplemer -
Echo & The Bunnymen - The Killing Moon!
Music • 3 • : Encia22
