It looks like you're using an Ad Blocker.
Please white-list or disable AboveTopSecret.com in your ad-blocking tool.
Thank you.
Some features of ATS will be disabled while you continue to use an ad-blocker.
share:
You've had a lot of your physics more or less right so far but I think you missed this one. If the photon lost energy it would in effect be red-shifted. I'm not familiar with that specific mirror setup but in general the way mirrors work is the energy lost is a fraction of the photons get absorbed in the mirror, but the ones that don't get absorbed usually don't lose energy:
Originally posted by dragonridr
what they mean is a mirror doesnt actually have a photon bounce off it. What happens when a photon hits a mirror is its absorbed by the mirror and then a new photon is created and off it goes. But the act of creating that new photon means each time theres a little less energy until eventually there isnt enough for the mirror to make a new one. We can go into detail if you want but thats basically whats going on.
How do mirrors reflect photons?
In a quantum-mechanical picture, light consists of photons, or packages of optical energy. The photons of the light reflected from a metal (or a dielectric mirror) are identical to the incident ones, apart from the changed propagation direction. The loss of light in the metal means that some fraction of the photons are lost, while the energy content of each reflected photon is fully preserved. Which of the photons are lost is a matter of chance; there is a certain probability for each photon to be absorbed.
Even if one photon in an entangled pair gets absorbed, that may destroy the entanglement, but it doesn't have to destroy the other photon. It will continue to exist unless it also gets absorbed, afaik.
reply to post by Arbitrageur
The fact reflection exists I do not understand very well. like if you have a light on in a bathroom and the bathroom is full of light and your looking in the mirror, how is the image so perfect if the light is constantly changing and scattering every which way and coming in and reflecting from all angles, is it being reflected off your face? Also the action of reflection; does the photons hit the electrons of the mirror, and the photons energy signature in a spectroscopy kinda way, have every bit of your face atoms ingraved in the light, and that information collides with the electrons in the mirror, and "reflects?" the photon information into your eye?
The fact reflection exists I do not understand very well. like if you have a light on in a bathroom and the bathroom is full of light and your looking in the mirror, how is the image so perfect if the light is constantly changing and scattering every which way and coming in and reflecting from all angles, is it being reflected off your face? Also the action of reflection; does the photons hit the electrons of the mirror, and the photons energy signature in a spectroscopy kinda way, have every bit of your face atoms ingraved in the light, and that information collides with the electrons in the mirror, and "reflects?" the photon information into your eye?
reply to post by ImaFungi
I don't see what this has to do with "Is faster than light communication possible?".
The previous discussion on mirrors was related to the topic on the idea that mirrors could be used in a possible FTL communication process where one of the entangled pair was absorbed by the mirror if I understand the idea.
I don't see what this has to do with "Is faster than light communication possible?".
The previous discussion on mirrors was related to the topic on the idea that mirrors could be used in a possible FTL communication process where one of the entangled pair was absorbed by the mirror if I understand the idea.
reply to post by dragonridr
Again, the same nonsense. All of this stems because some of you guys will not take the time to learn how entanglement works. Entanglement works because you can detect when entangled particle is measured.
So this communication is based on detection and even if they did a measurement, it would still be faster than light. The point is, they don't need to carry out a measurement because they're not trying to prove entanglement.
How do you think Quantum Communication works or how a Quantum Network will work if Network B doesn't know the information is coming from Network A? They know this because of entanglement. I will say this again. What you guys are describing isn't entanglement. You have to be able to DETECT when a measurement is being carried out on an entangled particle pair. Here's how one experiment was carried out.
phys.org...
This is from 2008 and this is exactly what I've been saying. Information isn't traveling from point A to point B. So detection and measurement take 7.1 microseconds. Again:
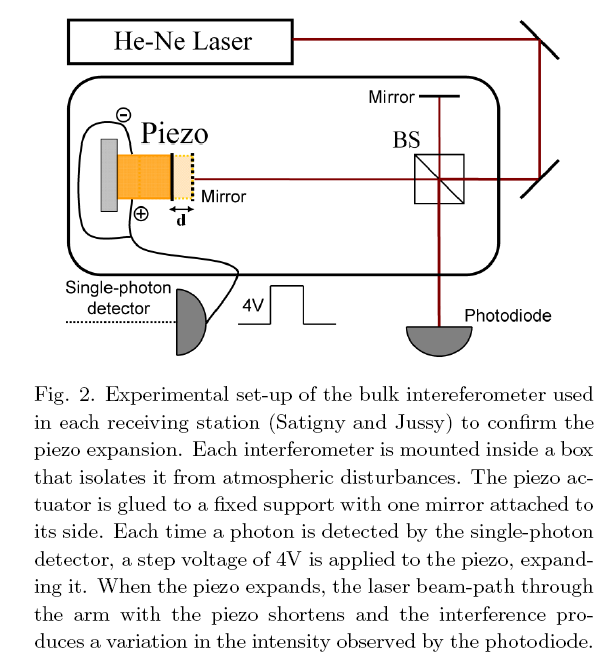
THE DETECTION OF EACH PHOTON TRIGGERS A VOLTAGE TO AN ACTUATOR WHICH CAUSE A MIRROR TO MOVE AND THIS TAKES 7.1 MICROSECONDS.
In this case you don't have to check for correlations because you're not trying to prove entanglement. You have detected Alice's particle pair.
Again, without DETECTION you don't have entanglement. How can you build a quantum network if you can't detect when network B is making a measurement on the entangled pair at network A? You can't build a quantum communication network if you don't know when entangled particle pairs are being measured.
Again, some of you guys don't understand entanglement.
This was also a test I like because it talked about Penrose-Diosi. Penrose also talks about quantum gravity and how it relates to Quantum Consciousness.
Again, the same nonsense. All of this stems because some of you guys will not take the time to learn how entanglement works. Entanglement works because you can detect when entangled particle is measured.
So this communication is based on detection and even if they did a measurement, it would still be faster than light. The point is, they don't need to carry out a measurement because they're not trying to prove entanglement.
How do you think Quantum Communication works or how a Quantum Network will work if Network B doesn't know the information is coming from Network A? They know this because of entanglement. I will say this again. What you guys are describing isn't entanglement. You have to be able to DETECT when a measurement is being carried out on an entangled particle pair. Here's how one experiment was carried out.
World's Largest Quantum Bell Test Spans Three Swiss Towns
In their experiment, the physicists sent pairs of entangled photons from Geneva through optical fibers leading to interferometers in two other Swiss towns: Satigny and Jussy, located 8.2 and 10.7 km away, respectively. The distance between the interferometers in Satigny and Jussy was 18 km.
With this large distance between the interferometers, the physicists could perform a more complete quantum measurement than has previously been done. Somewhat surprisingly, physicists have never decided exactly when a quantum measurement is finished (when the “collapse” occurs, if there is any).
Different interpretations of quantum mechanics lead to different answers. The most common view is that a quantum measurement is finished as soon as the photons are absorbed by detectors. Previous experiments have been set up to allow enough distance between particle detectors to prohibit communication under this view. But there are also other views of when the measurement is finished, including “when the result is secured in a classical system,” “when the information is in the environment,” or even that it is never over – a view that leads to the many worlds interpretation.
The Swiss team followed a view proposed independently by Penrose and Diosi, which assumes a connection between quantum measurements and gravity, and requires a macroscopic mass to be moved. In this view, the measurement takes more time than it does for a photon to be absorbed by a detector. The significance of the Swiss test is that it is the first “space-like separated” Bell test under the Penrose-Diosi assumption.
In the physicists’ experiment, the detection of each photon by a single-photon detector triggers a voltage to a piezoelectric actuator. The actuator expands, which in turn causes a tiny gold-surfaced mirror to move. By measuring the mirror displacement, the researchers could confirm by the gravity-quantum connection that the quantum measurement had been successfully finished.
All of the steps – from photon detection to mirror movement – take about 7.1 microseconds, which is significantly less than the 60 microseconds it would take a photon to cover the 18 km between interferometers. So measurements made simultaneously at each of the interferometers could not be been influenced by anything traveling at – or even a few times more than – the speed of light.
phys.org...
This is from 2008 and this is exactly what I've been saying. Information isn't traveling from point A to point B. So detection and measurement take 7.1 microseconds. Again:
THE DETECTION OF EACH PHOTON TRIGGERS A VOLTAGE TO AN ACTUATOR WHICH CAUSE A MIRROR TO MOVE AND THIS TAKES 7.1 MICROSECONDS.
In this case you don't have to check for correlations because you're not trying to prove entanglement. You have detected Alice's particle pair.
Again, without DETECTION you don't have entanglement. How can you build a quantum network if you can't detect when network B is making a measurement on the entangled pair at network A? You can't build a quantum communication network if you don't know when entangled particle pairs are being measured.
Again, some of you guys don't understand entanglement.
This was also a test I like because it talked about Penrose-Diosi. Penrose also talks about quantum gravity and how it relates to Quantum Consciousness.
reply to post by neoholographic
Ok so in the swiss experiment. They started at point A, and sent 2 entangled photons, one to point B and one to point C. From there I am a little confused. They made a measurement on a photon at point B or C, ( lets say B) or the photon arrived at their detector, and when it did that a change to photon on the path to C or arriving at C was detected?
Ok so in the swiss experiment. They started at point A, and sent 2 entangled photons, one to point B and one to point C. From there I am a little confused. They made a measurement on a photon at point B or C, ( lets say B) or the photon arrived at their detector, and when it did that a change to photon on the path to C or arriving at C was detected?
Thanks, it helps to have some specifics to look at.
They use the same detector at both locations as stated in the caption:
arxiv.org...
It is only by the third location comparing measurement results that correlations are established in the other two measurement sites.
The detector at one measurement site doesn't know what is going on at the detector at the other measurement site faster than light, as your FTL communication "magical detector" would permit.
"Bob" can find out slower than light that there were some correlations happening between the two sites much faster than light, but we already have fairly good slower than light communication methods like cell phones which communicate at nearly the speed of light.
In your idea Bob could somehow know which photons in the pairs Alice had observed and which she hadn't observed. But this actuator will move when each photon strikes it whether the entangled partner at the other end was observed at the other end or not. So it doesn't support your magical detector claim in any way, and in no way leads to any FTL communication nor does it claim to.
Originally posted by neoholographic
This is from 2008 and this is exactly what I've been saying. Information isn't traveling from point A to point B. So detection and measurement take 7.1 microseconds. Again:
THE DETECTION OF EACH PHOTON TRIGGERS A VOLTAGE TO AN ACTUATOR WHICH CAUSE A MIRROR TO MOVE AND THIS TAKES 7.1 MICROSECONDS.
In this case you don't have to check for correlations because you're not trying to prove entanglement. You have detected Alice's particle pair.
They use the same detector at both locations as stated in the caption:
arxiv.org...

It is only by the third location comparing measurement results that correlations are established in the other two measurement sites.
The detector at one measurement site doesn't know what is going on at the detector at the other measurement site faster than light, as your FTL communication "magical detector" would permit.
"Bob" can find out slower than light that there were some correlations happening between the two sites much faster than light, but we already have fairly good slower than light communication methods like cell phones which communicate at nearly the speed of light.
Originally posted by neoholographic
reply to post by dragonridr
Again, the same nonsense. All of this stems because some of you guys will not take the time to learn how entanglement works. Entanglement works because you can detect when entangled particle is measured.
Could you point us to the experiment where you show that photon entanglement works as a method of communication? Something which talks about how much data they transferred?
Those Dr Quantum videos on youtube are absolute poison, btw. Very misleading about the state of material reality.
edit on 16-5-2013 by yampa
because: (no reason given)
Let me guess...you're skeptical about the quantum channeling of Ramtha, the 35,000-year-old Lemurian warrior? Yeah, I am too, which is why I'm usually critical of those videos too and in fact I made a thread to not only criticize one of the clips from that movie, but to put its misrepresentation of the observer effect in perspective:
Originally posted by yampa
Those Dr Quantum videos on youtube are absolute poison, btw. Very misleading about the state of material reality.
The "observer effect": Is it proof the system is "aware it's being observed?"
However, as many problems as there are with many ridiculous claims in that movie, there is some real science mixed in and the particular clip neoholographic posted earlier didn't contain any huge discrepancies with observation and experiment that I recall. If it had, I think I would have complained about it.
I didn't really get into entanglement in my thread, but the observer effect is at the heart of why neoholographic's idea hasn't been done. There have been some clever attempts to get around the observer effect in quantum entanglement experiments, which is simply stated:
Observer effect (physics)
But even with these clever measurement schemes, none have yielded FTL communication, so far.
in quantum mechanics, which deals with very small objects, it is not possible to observe a system without changing the system
Originally posted by Arbitrageur
Let me guess...you're skeptical about the quantum channeling of Ramtha, the 35,000-year-old Lemurian warrior? Yeah, I am too, which is why I'm usually critical of those videos too and in fact I made a thread to not only criticize one of the clips from that movie, but to put its misrepresentation of the observer effect in perspective:
Originally posted by yampa
Those Dr Quantum videos on youtube are absolute poison, btw. Very misleading about the state of material reality.
The "observer effect": Is it proof the system is "aware it's being observed?"
However, as many problems as there are with many ridiculous claims in that movie, there is some real science mixed in and the particular clip neoholographic posted earlier didn't contain any huge discrepancies with observation and experiment that I recall. If it had, I think I would have complained about it.
I didn't really get into entanglement in my thread, but the observer effect is at the heart of why neoholographic's idea hasn't been done. There have been some clever attempts to get around the observer effect in quantum entanglement experiments, which is simply stated:
Observer effect (physics)
But even with these clever measurement schemes, none have yielded FTL communication, so far.
in quantum mechanics, which deals with very small objects, it is not possible to observe a system without changing the system
I'm sceptical about a lot of it, tbh. I don't like quantum mechanics and I think we can do much better,
I liked your comment:
So I think what I uncovered was an "observer effect" that the fatter probe has so much metal mass to it, that it actually acts like a heat sink and actually changes the temperature of what it's measuring
I think that sums up much of the observer effect, particularly with experiments like the dual slit. It has to be recognised that all matter is emitting energy in the form of particles. When your thermometer is heated it is bombarding the subject you are measuring with infrared radiation particles, changing the local dynamic. So yes, when you do this kind of thing with electrons, it is very easy to disturb the particle with the emitted 'charge' from your measuring instrument. Like you say, this can also work in reverse, where a 'less charged' sensor can act negatively or as a vacuum.
On the other hand. If you are smart about how you do your measurements, you can not only avoid disturbing the particle significantly - you can even do two measurements at once. Unavoidable recoil becomes avoidable and one of Heisenberg's postulates falls:
www.scientificamerican.com...
What Einstein's E=mc2 is to relativity theory, Heisenberg's uncertainty principle is to quantum mechanics—not just a profound insight, but also an iconic formula that even non-physicists recognize. The principle holds that we cannot know the present state of the world in full detail, let alone predict the future with absolute precision. It marks a clear break from the classical deterministic view of the universe.
Yet the uncertainty principle comes in two superficially similar formulations that even many practicing physicists tend to confuse. Werner Heisenberg's own version is that in observing the world, we inevitably disturb it. And that is wrong, as a research team at the Vienna University of Technology has now vividly demonstrated.
edit on 16-5-2013 by yampa because: (no reason given)
reply to post by neoholographic
I have been telling you over and over its you that doesn't understand how it works first this experiment you're using is not about entangled pairs what they are doing is quantifying what measurements or interactions are sufficient to destroy quantum decoherence. This is an important concept in quantum physics let me see if i can get you to understand. To start ill explain coherence here the way i look at this say we have 2 candles you place those candles at opposite ends of the room. Look at them compare their brightness. Now we take both and put them in one corner and again we look at them to us it looks brighter and if they're close it looks to us like only one flame. So lets say we have two or more particles and say their electrons that are in-phase they become a single wave function and as a side effect make a larger wave function out of phase well smaller but i can explain that another time. So just like to us we can't separate the two candles a detector see both particles as the same wave function. Now in this test they are testing decoherence and were trying to see when this wave function breaks down or if it does or it only acts like it does weird theory i wont go into . This is called interference some neat things this opens up including the star trek halo deck sort of because this can allow us to use light to create interference patterns in the middle of a room creating a full 3D effect no more TV. Or use this for quantum computing for storing photons until they can be used we need to know when or if wave form actually breaks down. If this doesn’t help i can try to explain again another way problem is when dealing with physics there’s a lot of background stuff that scientists assume you know and it makes it very hard to explain. To be honest I have taken lots of classes and theirs still a lot i don’t understand. But back on topic the one thing that’s making quantum communication impossible measuring 2 entangled particles ALL WE CAN DO IS CHECK THEM TO SEE WHAT STATE THEY DECIDE TO BE IN AND THE ONLY INFORMATION WE LEARN FROM THIS IS THERE BOTH IN THE SAME STATE. We cant change it we cant even tell if one particle is even still entangled. We can assume it is but then again the other person might have broken the entanglement and your particle is alone in the universe again.Now as I said before for communication there is one cool thing we can do with entangled pairs and thats create noise on a comunication and the other side can remove the noise because they have the other particle meaning you truly get secure communication between these two sites.
I have been telling you over and over its you that doesn't understand how it works first this experiment you're using is not about entangled pairs what they are doing is quantifying what measurements or interactions are sufficient to destroy quantum decoherence. This is an important concept in quantum physics let me see if i can get you to understand. To start ill explain coherence here the way i look at this say we have 2 candles you place those candles at opposite ends of the room. Look at them compare their brightness. Now we take both and put them in one corner and again we look at them to us it looks brighter and if they're close it looks to us like only one flame. So lets say we have two or more particles and say their electrons that are in-phase they become a single wave function and as a side effect make a larger wave function out of phase well smaller but i can explain that another time. So just like to us we can't separate the two candles a detector see both particles as the same wave function. Now in this test they are testing decoherence and were trying to see when this wave function breaks down or if it does or it only acts like it does weird theory i wont go into . This is called interference some neat things this opens up including the star trek halo deck sort of because this can allow us to use light to create interference patterns in the middle of a room creating a full 3D effect no more TV. Or use this for quantum computing for storing photons until they can be used we need to know when or if wave form actually breaks down. If this doesn’t help i can try to explain again another way problem is when dealing with physics there’s a lot of background stuff that scientists assume you know and it makes it very hard to explain. To be honest I have taken lots of classes and theirs still a lot i don’t understand. But back on topic the one thing that’s making quantum communication impossible measuring 2 entangled particles ALL WE CAN DO IS CHECK THEM TO SEE WHAT STATE THEY DECIDE TO BE IN AND THE ONLY INFORMATION WE LEARN FROM THIS IS THERE BOTH IN THE SAME STATE. We cant change it we cant even tell if one particle is even still entangled. We can assume it is but then again the other person might have broken the entanglement and your particle is alone in the universe again.Now as I said before for communication there is one cool thing we can do with entangled pairs and thats create noise on a comunication and the other side can remove the noise because they have the other particle meaning you truly get secure communication between these two sites.
Originally posted by neoholographic
reply to post by dragonridr
Again, the same nonsense. All of this stems because some of you guys will not take the time to learn how entanglement works. Entanglement works because you can detect when entangled particle is measured.
SNIP
Originally posted by neoholographic
Again, without DETECTION you don't have entanglement. How can you build a quantum network if you can't detect when network B is making a measurement on the entangled pair at network A? You can't build a quantum communication network if you don't know when entangled particle pairs are being measured.
Again, some of you guys don't understand entanglement.
A quantum network works by entangling photons and sending them directly to a detector at the transmission end and the receiving end. Data is transmitted using 'normal' means and would continue to work if the photons weren't entangled.
What the entangled photons achieve is security. By measuring the spin of the entangled photons you can tell if the communication photon has been been intercepted and retransmitted because the pattern of spins recorded for the message won't match for the sender and receiver.
Synchronisation is achieved by making the gaps between transmissions large enough to correlate the photon pairs.
edit on 17-5-2013 by EasyPleaseMe because: (no reason given)
The lack of understanding is astounding. I showed up above that we have to be able to know that particle A is being measured and influencing particle
B. If we didn't this wouldn't be entanglement. Again, listen to the videos.
Again, how would you know that a measurement on particle A influences particle B if you couldn't measure when particle B was detected and that it was the entangled pair of particle A? Like I keep saying, that's not entanglement.
Here's Dr. Michio Kaku saying information is sent faster than light. He just says the information isn't useful.
The thing is you don't only need to understand Entanglement but also information.
hhhttggbbbrddddeerruuu
This is still information it's just in a higher state of entropy as opposed to this:
Alice went to the park.
What Dr. Kaku is talking about is trying to send a morse code via entanglement. Well, you couldn't if you tried to say spin up is a + and spin down is a - .
You're just going to get random strings of information that's not useful.
With the QCD, each channel will carry entangled particles the equal 1 thing. So channel 1 would carry + and channel 2 would carry -.
Then instead of random + and - you could send useful information.
So if all entangled particles in channel 1 equals D and all the entangled particles in channel 2 Equal A and all the entangled particles in channel 3 equals N.
YOU CAN SEND THE WORD DAN FROM EARTH TO JUPITER FASTER THAN LIGHT!
Again, how would you know that a measurement on particle A influences particle B if you couldn't measure when particle B was detected and that it was the entangled pair of particle A? Like I keep saying, that's not entanglement.
Here's Dr. Michio Kaku saying information is sent faster than light. He just says the information isn't useful.
The thing is you don't only need to understand Entanglement but also information.
hhhttggbbbrddddeerruuu
This is still information it's just in a higher state of entropy as opposed to this:
Alice went to the park.
What Dr. Kaku is talking about is trying to send a morse code via entanglement. Well, you couldn't if you tried to say spin up is a + and spin down is a - .
You're just going to get random strings of information that's not useful.
With the QCD, each channel will carry entangled particles the equal 1 thing. So channel 1 would carry + and channel 2 would carry -.
Then instead of random + and - you could send useful information.
So if all entangled particles in channel 1 equals D and all the entangled particles in channel 2 Equal A and all the entangled particles in channel 3 equals N.
YOU CAN SEND THE WORD DAN FROM EARTH TO JUPITER FASTER THAN LIGHT!
He says you can't send "net information" and uses morse code as an example.
Originally posted by neoholographic
What Dr. Kaku is talking about is trying to send a morse code via entanglement. Well, you couldn't if you tried to say spin up is a + and spin down is a - .
Everybody else in this thread has been telling you the same thing as Michio Kaku. You seem to be the only one who doesn't get it. Yes entanglement is much faster than light, but no it can't be used to transmit "net information" to quote Dr. Kaku. Really you're making the ultimate insult to Dr. Kaku and other scientists if you think they can do that massively complex math but are unable to think of a morse code system that only uses dots which is what you're suggesting in effect (instead of dots and dashes).
If you can send "net information" FTL, then you should be working on collecting your Nobel prize by demonstrating it in experiment, instead of making claims here for which you have no evidence.
You're debunked by your own source.
When he says "probably not", you can interpret that the same as my qualifier that we can't be certain what future experiments might reveal. But we are pretty certain that experiments conducted to date have not sent any net information and have not revealed any means by which net information may be sent FTL.
reply to post by Arbitrageur
LOL,
Kaku actually supports what I'm saying when he says information can be sent faster than light.
Do you even know what he means when he says "net information"? What is he talking about and how do you define "net information"?
Also, what I described, how is that not sending "net information"?
LOL,
Kaku actually supports what I'm saying when he says information can be sent faster than light.
Do you even know what he means when he says "net information"? What is he talking about and how do you define "net information"?
Also, what I described, how is that not sending "net information"?
edit on 17-5-2013 by neoholographic because: (no reason given)
Kaku referred to sending a love letter FTL saying it can't be done (yet).
Originally posted by neoholographic
Kaku actually supports what I'm saying when he says information can be sent faster than light.
Do you even know what he means when he says "net information"? What is he talking about and how do you define "net information"?
Also, what I described, how is that sending "net information"?
You referred to sending text messages FTL:
www.abovetopsecret.com...
Originally posted by neoholographic
If you had 24 channels on the QCD, you can send text messages to each other faster than light from anywhere in the universe.
Kaku's love letter example and your FTL text messages would be "net information". This is what Kaku and everybody else except you has been trying to get across:
Quantum Teleportation
There's a lot of semantics going on in the terminology of "information" and "communication", but perhaps the simplest definition would be to say nothing "useful" is received faster than light.
Quantum teleportation, or entanglement-assisted teleportation, is a process by which a qubit (the basic unit of quantum information) can be transmitted exactly (in principle) from one location to another, without the qubit being transmitted through the intervening space. It is useful for quantum information processing. However, it does not immediately transmit classical information, and therefore cannot be used for communication at superluminal (faster than light) speed.
In quantum computer systems, there is quantum information received faster than light, and it's used eventually, but it doesn't become useful until later, when a fiber optic or similar classical communication channel makes the information useful, as EasyPleaseMe described here:
www.abovetopsecret.com...
edit on 17-5-2013 by Arbitrageur because: clarification
Originally posted by neoholographic
This video makes me think it can be our understanding or interpretation of quantum mechanics that allows entanglement to exist, when really it doesnt in the manner you think it does.
In his example of indeterminate states he uses 'red' and 'blue'. What if instead of creating entangled particles, the particles are in indeterminate superposition states, and we measure one and the other one FTL changes to the opposite. What makes people not think that when an entangled pair of particles are created, one is red and one is blue, and when we measure the red one, that means the other is blue? Not that it is instantly turning to blue just because we were ignorant of the states before measuring.
reply to post by neoholographic
Ok last try there is a reason no useful information can be transferred will again have are entangled electrons we take them to the other side of the galaxy.And we turn on our machines to observe these particles. We see electrons moving we know the other particle at this moment is doing the exact same thing but the problem becomes what there doing is totally random. Until we observe the particle its doing everything all at once we look at it through a measurement to say check spin or check momentum etc then the particle tells us what state it chose to be in.We could have 1 particle for every letter of the alphabet problem is because the particle state in random we have no idea which particle was supposed to be the letter in our message. Now the kicker measuring the particle its self breaks entanglement in fact its a ver fragile state. Now if thats not enough theres another reason as well you never know which particle is copying the other. So lets say we measure spin i have a particle and you do we take our measurements mines spin up yours is spin down now how do we know which particle actually chose the state and transfered the information to the other one??? my particle could have decided spin up told yours and it went spin down or your particle could have decided and my particle just copied it theres no way to know.
Where it does come in handy as ive said multiple times is secure communications between 2 locations because we can use entangled pairs to make sure no one but us looked at the light pulses. This is important even in quantum computing because its a natural check sum for the information,In a computer it constantly checks to make sure the bits of information are right if there not it throws it out and is sent again. With light pulses we can make sure the light pulses are correct by checking both to make sure they are indeed the same. If they are great if not start over. So it has great possibilities for communication but not faster then light.
Ok last try there is a reason no useful information can be transferred will again have are entangled electrons we take them to the other side of the galaxy.And we turn on our machines to observe these particles. We see electrons moving we know the other particle at this moment is doing the exact same thing but the problem becomes what there doing is totally random. Until we observe the particle its doing everything all at once we look at it through a measurement to say check spin or check momentum etc then the particle tells us what state it chose to be in.We could have 1 particle for every letter of the alphabet problem is because the particle state in random we have no idea which particle was supposed to be the letter in our message. Now the kicker measuring the particle its self breaks entanglement in fact its a ver fragile state. Now if thats not enough theres another reason as well you never know which particle is copying the other. So lets say we measure spin i have a particle and you do we take our measurements mines spin up yours is spin down now how do we know which particle actually chose the state and transfered the information to the other one??? my particle could have decided spin up told yours and it went spin down or your particle could have decided and my particle just copied it theres no way to know.
Where it does come in handy as ive said multiple times is secure communications between 2 locations because we can use entangled pairs to make sure no one but us looked at the light pulses. This is important even in quantum computing because its a natural check sum for the information,In a computer it constantly checks to make sure the bits of information are right if there not it throws it out and is sent again. With light pulses we can make sure the light pulses are correct by checking both to make sure they are indeed the same. If they are great if not start over. So it has great possibilities for communication but not faster then light.
No, information cannot be transferred faster than light. I know quantum entanglement sounds like it should enable this, but it cannot. Using
it, you may be able to know about something so far away, that communicating it at the speed of light would take longer, but simply knowing about
something does not necessarily transfer information.
Originally posted by Subterranean13
No, information cannot be transferred faster than light. I know quantum entanglement sounds like it should enable this, but it cannot. Using it, you may be able to know about something so far away, that communicating it at the speed of light would take longer, but simply knowing about something does not necessarily transfer information.
The concept FTL transfer of information, in the most general sense refers to the physical material of the universe and its position in spacetime as information itself. I have a rock in my hand composed of particles, I throw it, there are physical laws and materials in its path that affects what happens, a few feet away it hits another rock, the rock traveled at a velocity, distance per unit of time, and this was much slower then the velocity at which light travels. In order for the rock on the ground that was hit by the rock I through, to have been hit, something had to hit it, physical information had to traverse space and time, to physically affect the rock.
When einstein says 'spooky action at a distance', and physicists say information is transferred FTL, this refers to the interpretation of quantum mechanics known as entanglement.
If entanglement is actually real, if two particles are created, and 'entangled', and one is measured, and its entangled partner "knows" what the result of the measurement on its partner is, then 'somehow', 'information' is being transferred across the universe at FTL speed.
I dont believe this. I believe physcists and arm chair physcists who think that scrhodingers cat is reality and not just schrodingers thought experiment showing how silly the notion of entanglement and superposition and FTL information transfer is, are wrong.
I think that when "entangled" particles are created, particles are created which have exact wavefunctions and energy potentials and states, but until measured, we cant possibly know what those variables are for either particle. Because the two particles are created in one instant, one bundle of energy, an event takes place with physical variables of momentum, mass, velocity, and the 2 'entangled' particles are birthed from that event each with their personal characteristics, when one is measured, the other must then have the other required qualities.
the number '3' is turned into a pair of entangled particles.... the two particles are sent to different places, physicists do not know which particle has which characteristics. One of the particles is measured and the particles qualities = 2... Instantly it is known that the entangled pair particle = 1.
Physicists who believe in entanglement, believe that the two entangled particles each are 1,2 and 3, all the time, never, and in increments. They believe when they measure the first and it = 2, that that particle then FTL across space and time "some freaking how", signals its entangled pair, and tells it it must =1. Im on Einsteins side... I admit I havent looked into entanglement too much, I asked NEO if there are any theoretical mechanisms that describe how entanglement may work, but I didnt see much that made sense to me, I admit the fault may lie with me, but it might not.
If you forget wave mechanics and impose the condition that photons are particles, all this talk of photonic entanglement goes away. There is no way
for one particle of light to influence another particle without either colliding with it or emitting something from itself. The idea that there is a
hidden, immediate virtual messenger particle is stupid and magical. We must look for real probable causes of this apparent 'paradox'.
How about, for instance - the fact we do not properly understand the fundamental motions of photons!
Instead of wandering into the fantasy mathematics of Quantum Mechanics, we might come up with an idea based on the real physical motion of photons? How about, for instance, recognising the complex angular motion of photons?
How could these observed complex motions be included in Quantum Mechanics if they weren't recognised until the 90s? Might the assumptions of Quantum Mechanics be based on incomplete but essential data?
Orbital momentum of light
www.gla.ac.uk...
OAM = -1 hbar per photon (right-hand
helical phase front)OAM = 0(plane wave)OAM = +1 hbar per
photon (left-hand helix)OAM = +2 hbar per photon (two-fold helix)OAM = +3 hbar per photon (three-fold helix: fusilli)
How about, for instance - the fact we do not properly understand the fundamental motions of photons!
Instead of wandering into the fantasy mathematics of Quantum Mechanics, we might come up with an idea based on the real physical motion of photons? How about, for instance, recognising the complex angular motion of photons?
How could these observed complex motions be included in Quantum Mechanics if they weren't recognised until the 90s? Might the assumptions of Quantum Mechanics be based on incomplete but essential data?
Orbital momentum of light
www.gla.ac.uk...
It has been known since the middle ages that light exerts a radiation pressure. Not so well known is that light also exerts a twist.
The intricate nature of this twist was not recognised until the 1990s and we have been working on it ever since. Beyond the fascination of setting microscopic objects into rotation, this orbital angular momentum may hold the key to better communication sensing and imaging systems.
Orbital Angular Momentum (OAM)
The phase fronts of light beams in orbital angular momentum (OAM) eigenstates rotate, clockwise for positive OAM values, anti-clockwise for negative values. The phase front with 0 OAM doesn't rotate at all.
OAM = -1 hbar per photon (right-hand
helical phase front)OAM = 0(plane wave)OAM = +1 hbar per
photon (left-hand helix)OAM = +2 hbar per photon (two-fold helix)OAM = +3 hbar per photon (three-fold helix: fusilli)
new topics
-
Any one suspicious of fever promotions events, major investor Goldman Sachs card only.
The Gray Area: 1 hours ago -
God's Righteousness is Greater than Our Wrath
Religion, Faith, And Theology: 6 hours ago -
Electrical tricks for saving money
Education and Media: 9 hours ago -
VP's Secret Service agent brawls with other agents at Andrews
Mainstream News: 10 hours ago -
Sunak spinning the sickness figures
Other Current Events: 11 hours ago -
Nearly 70% Of Americans Want Talks To End War In Ukraine
Political Issues: 11 hours ago
top topics
-
VP's Secret Service agent brawls with other agents at Andrews
Mainstream News: 10 hours ago, 9 flags -
Cats Used as Live Bait to Train Ferocious Pitbulls in Illegal NYC Dogfighting
Social Issues and Civil Unrest: 14 hours ago, 8 flags -
Electrical tricks for saving money
Education and Media: 9 hours ago, 4 flags -
Nearly 70% Of Americans Want Talks To End War In Ukraine
Political Issues: 11 hours ago, 3 flags -
Sunak spinning the sickness figures
Other Current Events: 11 hours ago, 3 flags -
Late Night with the Devil - a really good unusual modern horror film.
Movies: 13 hours ago, 2 flags -
Any one suspicious of fever promotions events, major investor Goldman Sachs card only.
The Gray Area: 1 hours ago, 2 flags -
The Good News According to Jesus - Episode 1
Religion, Faith, And Theology: 16 hours ago, 1 flags -
God's Righteousness is Greater than Our Wrath
Religion, Faith, And Theology: 6 hours ago, 0 flags
active topics
-
God's Righteousness is Greater than Our Wrath
Religion, Faith, And Theology • 12 • : randomuser2034 -
SETI chief says US has no evidence for alien technology. 'And we never have'
Aliens and UFOs • 61 • : andy06shake -
The Reality of the Laser
Military Projects • 47 • : F2d5thCavv2 -
Definitive 9.11 Pentagon EVIDENCE.
9/11 Conspiracies • 423 • : Lazy88 -
Election Year 2024 - Interesting Election-Related Tidbits as They Happen.
2024 Elections • 73 • : Threadbarer -
Sunak spinning the sickness figures
Other Current Events • 8 • : McUrnsalso -
-@TH3WH17ERABB17- -Q- ---TIME TO SHOW THE WORLD--- -Part- --44--
Dissecting Disinformation • 661 • : Justoneman -
HORRIBLE !! Russian Soldier Drinking Own Urine To Survive In Battle
World War Three • 36 • : TheMisguidedAngel -
British TV Presenter Refuses To Use Guest's Preferred Pronouns
Education and Media • 146 • : Consvoli -
Nearly 70% Of Americans Want Talks To End War In Ukraine
Political Issues • 19 • : Consvoli





