It looks like you're using an Ad Blocker.
Please white-list or disable AboveTopSecret.com in your ad-blocking tool.
Thank you.
Some features of ATS will be disabled while you continue to use an ad-blocker.
7
share:
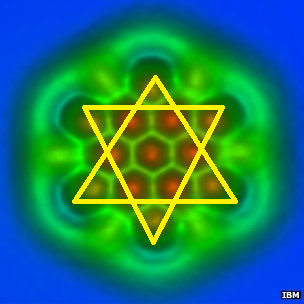
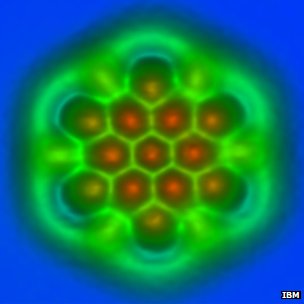
A pioneering team from IBM in Zurich has published single-molecule images so detailed that the type of atomic bonds between their atoms can be discerned.
The same team took the first-ever single-molecule image in 2009 and more recently published images of a molecule shaped like the Olympic rings.
The new work opens up the prospect of studying imperfections in the "wonder material" graphene or plotting where electrons go during chemical reactions.
Wow, just wow. I never actually though it was possible to see this small, It does not look like they are using visible light to do it?
We can see the BONDS between atoms! I saw the previous fuzzy picture af a molecule that they made, but this is its HD big brother
Link to Source
reply to post by DJOldskool
the hexagonal shape looks cool.


the hexagonal shape looks cool.

edit on 14-9-2012 by Samuelis because: pic
truly amazing, thank you very much for the post, i must say i am so excited to see
us enter the age of the mastery of the atom, i truly hope this technology leads to
amazing new things for all mankind. this is one of the steps in a personal
fabrication unit, that will truly change the world.
us enter the age of the mastery of the atom, i truly hope this technology leads to
amazing new things for all mankind. this is one of the steps in a personal
fabrication unit, that will truly change the world.
It says:
Originally posted by DJOldskool
It does not look like they are using visible light to do it?
That makes me wonder how they made the tip small enough. After all, they are scanning atoms, and the tip itself has to be made of atoms also, so the structure and size of this tip isn't entirely clear to me after reading the article.
The team, which included French and Spanish collaborators, used a variant of a technique called atomic force microscopy, or AFM.
AFM uses a tiny metal tip passed over a surface, whose even tinier deflections are measured as the tip is scanned to and fro over a sample.
Nice find, it's pretty amazing!
Keep an open mind they could be just projecting these images A prioi.
Looks a lot like a Bee hive so it might not be new.
Looks a lot like a Bee hive so it might not be new.
edit on 14-9-2012 by Cauliflower because: Well, there's hours of time on the telephone
line to talk about things to come
Originally posted by Arbitrageur
It says:
Originally posted by DJOldskool
It does not look like they are using visible light to do it?
That makes me wonder how they made the tip small enough. After all, they are scanning atoms, and the tip itself has to be made of atoms also, so the structure and size of this tip isn't entirely clear to me after reading the article.
The team, which included French and Spanish collaborators, used a variant of a technique called atomic force microscopy, or AFM.
AFM uses a tiny metal tip passed over a surface, whose even tinier deflections are measured as the tip is scanned to and fro over a sample.
Nice find, it's pretty amazing!
The tip has to end somewhere and there will be an atom where it ends. Usually, cutting it on a diagonal will do the trick for a STEM.
reply to post by Arbitrageur
Disclaimer: Not a Physicist but am studying it.
IMO. On the end of that tip is a singe carbon-monoxide molecule. This molecule becomes a dipole and is ever so slightly repelled or attracted by the matter it is scanning over. I take they build the picture from the vibrations recorded through the 'needle'.
No wonder they need to account for the earths natural vibration and cool the equipment to -268C
Disclaimer: Not a Physicist but am studying it.
IMO. On the end of that tip is a singe carbon-monoxide molecule. This molecule becomes a dipole and is ever so slightly repelled or attracted by the matter it is scanning over. I take they build the picture from the vibrations recorded through the 'needle'.
No wonder they need to account for the earths natural vibration and cool the equipment to -268C
Dr. Hell of the German Max Planck Society got a European Union award last year for making a microscope to see smaller than mankind has ever seen.
Der Germans are ahead of everyone else in seeing Atoms. Fitting name for what horror will come from his invention.
Der Germans are ahead of everyone else in seeing Atoms. Fitting name for what horror will come from his invention.
It really blows me away, the fact that the macro world of vast space is such a vast space and such a mystery that we can only view from afar, and the
micro of which we can get so close to, yet also so far away.
From the big to the small is where all the mysteries of the Universe are located.
What they do is like laser scanning of sorts, like scanning the ocean floor with sonar etc. After all, how can they see this stuff with lenses, when the lenses themselves are made up off molecules?
From the big to the small is where all the mysteries of the Universe are located.
What they do is like laser scanning of sorts, like scanning the ocean floor with sonar etc. After all, how can they see this stuff with lenses, when the lenses themselves are made up off molecules?
reply to post by Pervius
The Germans have always had a great recognition by having the best manufactures of precision instrumentation. This has even rubbed off on how the world looks at Germans, even before WW2.
During WW2 the inventiveness and technical capability was put to work on the war effort, but not all many scientists and experts left Germany to other nations (Switzerland, UK, Canada and US for instance). Most of the advances in technology seen by the US have been spearheaded by immigrants (not only from Germany). There is the famous peper-clip program and others...
Today you need not look much further than the interest China demonstrates in some of Germany's firms in regards to acquisitions and partnerships.
The Germans have always had a great recognition by having the best manufactures of precision instrumentation. This has even rubbed off on how the world looks at Germans, even before WW2.
During WW2 the inventiveness and technical capability was put to work on the war effort, but not all many scientists and experts left Germany to other nations (Switzerland, UK, Canada and US for instance). Most of the advances in technology seen by the US have been spearheaded by immigrants (not only from Germany). There is the famous peper-clip program and others...
Today you need not look much further than the interest China demonstrates in some of Germany's firms in regards to acquisitions and partnerships.
www.flickr.com/photos/ibm_research_zurich/7979701269/in/set-72157631317472684
Bond Order Discrimination (animation)
Animation showing the last cooper atom of the tip of the Atomic Force Microscope (top) where a carbon-monoxide molecule are terminated. The carbon atoms are blue and the oxygen atom is red. This tip oscillates with a tiny amplitude above the C60, known as a buckyball, and the forces are measured between of the two molecules, to create an image. The carbon-monoxide termination of the tip acts as a powerful magnifying glass to reveal the atomic structure of the molecule, including its bonds.
new topics
-
Late Night with the Devil - a really good unusual modern horror film.
Movies: 15 minutes ago -
Cats Used as Live Bait to Train Ferocious Pitbulls in Illegal NYC Dogfighting
Social Issues and Civil Unrest: 1 hours ago -
The Good News According to Jesus - Episode 1
Religion, Faith, And Theology: 3 hours ago -
HORRIBLE !! Russian Soldier Drinking Own Urine To Survive In Battle
World War Three: 5 hours ago -
Bobiverse
Fantasy & Science Fiction: 8 hours ago -
Florida man's trip overseas ends in shock over $143,000 T-Mobile phone bill
Social Issues and Civil Unrest: 8 hours ago -
Former Labour minister Frank Field dies aged 81
People: 10 hours ago
top topics
-
President BIDEN Vows to Make Americans Pay More Federal Taxes in 2025 - Political Suicide.
2024 Elections: 17 hours ago, 19 flags -
Florida man's trip overseas ends in shock over $143,000 T-Mobile phone bill
Social Issues and Civil Unrest: 8 hours ago, 8 flags -
SETI chief says US has no evidence for alien technology. 'And we never have'
Aliens and UFOs: 12 hours ago, 7 flags -
Cats Used as Live Bait to Train Ferocious Pitbulls in Illegal NYC Dogfighting
Social Issues and Civil Unrest: 1 hours ago, 4 flags -
Former Labour minister Frank Field dies aged 81
People: 10 hours ago, 4 flags -
Bobiverse
Fantasy & Science Fiction: 8 hours ago, 3 flags -
This is our Story
General Entertainment: 15 hours ago, 3 flags -
HORRIBLE !! Russian Soldier Drinking Own Urine To Survive In Battle
World War Three: 5 hours ago, 2 flags -
Late Night with the Devil - a really good unusual modern horror film.
Movies: 15 minutes ago, 1 flags -
The Good News According to Jesus - Episode 1
Religion, Faith, And Theology: 3 hours ago, 0 flags
active topics
-
-@TH3WH17ERABB17- -Q- ---TIME TO SHOW THE WORLD--- -Part- --44--
Dissecting Disinformation • 650 • : angelchemuel -
Thousands Of Young Ukrainian Men Trying To Flee The Country To Avoid Conscription And The War
Other Current Events • 135 • : twistedpuppy -
President BIDEN Vows to Make Americans Pay More Federal Taxes in 2025 - Political Suicide.
2024 Elections • 89 • : DBCowboy -
Late Night with the Devil - a really good unusual modern horror film.
Movies • 0 • : devilhunter69 -
New whistleblower Jason Sands speaks on Twitter Spaces last night.
Aliens and UFOs • 52 • : 0bserver1 -
SETI chief says US has no evidence for alien technology. 'And we never have'
Aliens and UFOs • 33 • : 0bserver1 -
Mood Music Part VI
Music • 3099 • : BrucellaOrchitis -
HORRIBLE !! Russian Soldier Drinking Own Urine To Survive In Battle
World War Three • 20 • : budzprime69 -
Cats Used as Live Bait to Train Ferocious Pitbulls in Illegal NYC Dogfighting
Social Issues and Civil Unrest • 2 • : Cre8chaos79 -
Florida man's trip overseas ends in shock over $143,000 T-Mobile phone bill
Social Issues and Civil Unrest • 14 • : Raptured
7